Options Payoffs and Profits & Losses (Calculations for CFA® and FRM® Exams)
AnalystPrep's Concept Capsules for CFA® and FRM® Exams
This series of video lessons is intended to review the main calculations required in your CFA and FRM exams.
For Level I Video Lessons, Study Notes, Question Bank, CBT Mock Exams & More: https://analystprep.com/shop/cfa-level-1-learn-practice-package/
For FRM (Part I & Part II) Video Lessons, Study Notes, Question Bank, CBT Mock Exams & More: https://analystprep.com/shop/unlimited-package-for-frm-part-i-part-ii/
*AnalystPrep is an Official GARP-Approved Exam Preparation Provider*
Options
The buyer of an option has the right but not the obligation to exercise the option. The maximum loss to the buyer is equal to the premium paid for the option. The potential gains are theoretically infinite. To the seller (writer), however, the maximum gain is limited to the premium received after writing the option. The potential loss is unlimited.
In an options contract, two parties transact simultaneously. The buyer of a call or a put option is the long position in the contract while the seller of the option, also known as the writer of the option, is the short position.
Long vs. Short
Here is it important to differentiate between the long and the short party in a contract. The buyer is always said to be long the option. This is quite easy to see for a call option.
However, for a put option, the long position in a put is betting that the underlying price will drop. As such, the long position in a put option is synonymous to being short the underlying.
Expiration
Exchange-traded stock options can either be American or European style. While European options can only be exercised at expiry, American options can be exercised at any point during the life of the option. The actual date of expiry is specified by the exchange.
Strike Prices
Тhe value of the stock directly controls the strike price. At the expiration date, the difference between the stock’s market price and the option’s strike price determines the payoff.
Moneyness
For Call Options:
▪ If the stock price exceeds the exercise price, the option is in-the-money (ITM).
▪ If the stock price is less than the exercise price, the option is out-of-the-money (OTM).
▪ If the current market price is equal to the strike price, the option is at-the-money (ATM).
For Put Options: Just the opposite
▪ If the stock price is less than exercise price, the option is in-the-money (ITM).
▪ If the stock price exceeds the exercise price, the option is out-of-the-money (OTM).
▪ If the current market price is equal to the strike price, the option is at-the-money (ATM).
Intrinsic Value and Time Value
The intrinsic value of an option is the difference between the prevailing market price of the underlying and the strike price.
▪ Intrinsic value of a call option = max(0, St − X)
▪ Intrinsic value of a put option = max(0, X − St)
Видео Options Payoffs and Profits & Losses (Calculations for CFA® and FRM® Exams) канала AnalystPrep
This series of video lessons is intended to review the main calculations required in your CFA and FRM exams.
For Level I Video Lessons, Study Notes, Question Bank, CBT Mock Exams & More: https://analystprep.com/shop/cfa-level-1-learn-practice-package/
For FRM (Part I & Part II) Video Lessons, Study Notes, Question Bank, CBT Mock Exams & More: https://analystprep.com/shop/unlimited-package-for-frm-part-i-part-ii/
*AnalystPrep is an Official GARP-Approved Exam Preparation Provider*
Options
The buyer of an option has the right but not the obligation to exercise the option. The maximum loss to the buyer is equal to the premium paid for the option. The potential gains are theoretically infinite. To the seller (writer), however, the maximum gain is limited to the premium received after writing the option. The potential loss is unlimited.
In an options contract, two parties transact simultaneously. The buyer of a call or a put option is the long position in the contract while the seller of the option, also known as the writer of the option, is the short position.
Long vs. Short
Here is it important to differentiate between the long and the short party in a contract. The buyer is always said to be long the option. This is quite easy to see for a call option.
However, for a put option, the long position in a put is betting that the underlying price will drop. As such, the long position in a put option is synonymous to being short the underlying.
Expiration
Exchange-traded stock options can either be American or European style. While European options can only be exercised at expiry, American options can be exercised at any point during the life of the option. The actual date of expiry is specified by the exchange.
Strike Prices
Тhe value of the stock directly controls the strike price. At the expiration date, the difference between the stock’s market price and the option’s strike price determines the payoff.
Moneyness
For Call Options:
▪ If the stock price exceeds the exercise price, the option is in-the-money (ITM).
▪ If the stock price is less than the exercise price, the option is out-of-the-money (OTM).
▪ If the current market price is equal to the strike price, the option is at-the-money (ATM).
For Put Options: Just the opposite
▪ If the stock price is less than exercise price, the option is in-the-money (ITM).
▪ If the stock price exceeds the exercise price, the option is out-of-the-money (OTM).
▪ If the current market price is equal to the strike price, the option is at-the-money (ATM).
Intrinsic Value and Time Value
The intrinsic value of an option is the difference between the prevailing market price of the underlying and the strike price.
▪ Intrinsic value of a call option = max(0, St − X)
▪ Intrinsic value of a put option = max(0, X − St)
Видео Options Payoffs and Profits & Losses (Calculations for CFA® and FRM® Exams) канала AnalystPrep
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Company Analysis: Past and Present (2024 CFA® Level I Exam – Equity – Learning Module 5)
Company Analysis: Past and Present (2024 CFA® Level I Exam – Equity – Learning Module 5) Getting up to Speed on the Financial Crisis (FRM Part 1 – Book 1 – Chapter 8)
Getting up to Speed on the Financial Crisis (FRM Part 1 – Book 1 – Chapter 8) Corporate Bonds (FRM Part 1 2023 – Book 3 – Chapter 20)
Corporate Bonds (FRM Part 1 2023 – Book 3 – Chapter 20) Evaluate the Argument (GMAT Course – Critical Reasoning Tactics – Common Question Tasks)
Evaluate the Argument (GMAT Course – Critical Reasoning Tactics – Common Question Tasks) Modeling Backsolving (GMAT Course – Overview & Question Types)
Modeling Backsolving (GMAT Course – Overview & Question Types) Interest (GMAT Focus Edition – Quantitative Reasoning Content and Tactics)
Interest (GMAT Focus Edition – Quantitative Reasoning Content and Tactics) Case Study in Risk Management: Private Wealth (2024 Level III CFA® – Reading 15)
Case Study in Risk Management: Private Wealth (2024 Level III CFA® – Reading 15) Verb Tenses (Executive Assessment Course – Sentence Corrections – Addressing Common Issues)
Verb Tenses (Executive Assessment Course – Sentence Corrections – Addressing Common Issues) Bayes Theorem Example (SOA Exam P – Probability – General Probability Module)
Bayes Theorem Example (SOA Exam P – Probability – General Probability Module) Infrastructure (2025 Level III CFA® – Private Markets – Learning Module 7)
Infrastructure (2025 Level III CFA® – Private Markets – Learning Module 7) Basic Argumentation (GMAT Focus Edition – Verbal Reasoning Content and Tactics)
Basic Argumentation (GMAT Focus Edition – Verbal Reasoning Content and Tactics)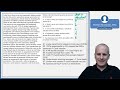 Dense Passages (GMAT Focus Edition – Verbal Reasoning Content and Tactics)
Dense Passages (GMAT Focus Edition – Verbal Reasoning Content and Tactics) Explain an Outcome (GMAT Course – Critical Reasoning Tactics – Common Question Tasks)
Explain an Outcome (GMAT Course – Critical Reasoning Tactics – Common Question Tasks) Identify the Flaw (GMAT Course – Critical Reasoning Tactics – Common Question Tasks)
Identify the Flaw (GMAT Course – Critical Reasoning Tactics – Common Question Tasks) Asset Allocation to Alternative Investments – Part II (2024 Level III CFA® – Reading 19)
Asset Allocation to Alternative Investments – Part II (2024 Level III CFA® – Reading 19) Summing Independent Random Variable (SOA Exam P – Probability – Multivariate Random Variables)
Summing Independent Random Variable (SOA Exam P – Probability – Multivariate Random Variables) Corporate Governance Conflicts, Mechanisms, Risks, and Benefits (2024 CFA® Level I Exam – CI – LM3)
Corporate Governance Conflicts, Mechanisms, Risks, and Benefits (2024 CFA® Level I Exam – CI – LM3) Covariance and Correlation (SOA Exam P – Probability – Multivariate Random Variables)
Covariance and Correlation (SOA Exam P – Probability – Multivariate Random Variables) Pricing and Valuation of Options (2024 Level I CFA® Exam – Derivatives – Module 8)
Pricing and Valuation of Options (2024 Level I CFA® Exam – Derivatives – Module 8) Boldfaced Statements (GMAT Focus Edition – Verbal Reasoning Content and Tactics)
Boldfaced Statements (GMAT Focus Edition – Verbal Reasoning Content and Tactics) Annuity Notation (Actuarial Exam FM – Financial Mathematics – Module 2, Section 1, Part 2)
Annuity Notation (Actuarial Exam FM – Financial Mathematics – Module 2, Section 1, Part 2)