Femoral Artery Anatomy | Origin | Branches | Clinical
The femoral artery is a continuation of the external iliac artery and constitutes the major blood supply to the lower limb. In the thigh, the femoral artery passes through the femoral triangle, a wedge-shaped depression formed by muscles in the upper thigh. The medial and lateral boundaries of this triangle are formed by the medial margin of adductor longus and the medial margin of sartorius, respectively.
Fascia lata constitutes the roof of the femoral triangle, whilst the floor is formed by pectineus and adductor longus medially as well as by iliacus and psoas major laterally. Within this triangle, the femoral artery is enclosed in a femoral sheath with the femoral vein. The femoral artery and its branches supply most of the thigh as well as the entirety of the leg and foot.
course
Midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis, the external iliac artery passes under the inguinal ligament into the femoral triangle and becomes the femoral artery. The artery then travels down the anteromedial aspect of the thigh before it passes through the adductor (subsartorial) canal. When the femoral artery passes through the adductor hiatus it becomes the popliteal artery.
Branches
The femoral artery gives off five branches in the femoral triangle and one in the adductor canal, to give six in total. These branches are described below.
Superficial epigastric artery
Superficial epigastric artery (Arteria epigastrica superficialis); Image: Rebecca Betts
Superficial epigastric artery (Arteria epigastrica superficialis)
The superficial epigastric artery arises from the femoral artery, 1 cm distal to the inguinal ligament. It travels through the cribiform fascia and ascends towards the umbilicus within the abdominal superficial fascia. It supplies the skin, superficial fascia and superficial inguinal lymph nodes.
Superficial circumflex iliac artery
The superficial circumflex iliac artery is the smallest branch of the femoral artery. It arises near the superficial epigastric artery. Lateral to the saphenous opening, the artery passes through the fascia lata before coursing towards the anterior superior iliac spine. Like the superficial epigastric artery, it supplies the skin, superficial fascia and superficial inguinal lymph nodes.
Superficial external pudendal artery
The superficial external pudendal artery arises near the superficial epigastric and superficial circumflex iliac arteries. It travels through the cribiform fascia before crossing the spermatic cord deep to the long saphenous vein. It supplies the lower abdominal skin as well as the penile, scrotal or labial skin.
Deep external pudendal artery
The deep external pudendal artery crosses the pectineus and adductor longus muscles before traversing the fascia lata. It supplies the skin of the perineum as well as the skin of the scrotum or labium majus.
Profunda femoris
Deep femoral artery (Arteria profunda femoris); Image: Liene Znotina
Deep femoral artery (Arteria profunda femoris)
Profunda femoris, also known as the deep artery of the thigh is the largest branch of the femoral artery, which arises 3.5 cm distal to the inguinal ligament. The profunda femoris is initially found lateral to the femoral artery before it passes deep to it towards the medial aspect of the femur. It travels between the pectineus and adductor longus muscles before passing between the adductor longus and adductor brevis muscles. It then descends between the adductor longus and adductor magnus muscles before it pierces the adductor magnus to anastamose with the muscular branches of the popliteal artery. The profunda femoris is the main blood supply to the muscles that extend, flex and adduct the thigh.
Descending genicular artery
Descending genicular artery is the most distal branch of the femoral artery, which arises just proximal to the adductor opening within the adductor canal. It descends within the vastus medialis muscle to the medial aspect of the knee. Here, it anastomoses with the medial superior genicular artery. Branches of this artery supply the vastus medialis and adductor magnus muscles as well as the proximomedial skin of the thigh.
Видео Femoral Artery Anatomy | Origin | Branches | Clinical канала Knowing Anatomy
Fascia lata constitutes the roof of the femoral triangle, whilst the floor is formed by pectineus and adductor longus medially as well as by iliacus and psoas major laterally. Within this triangle, the femoral artery is enclosed in a femoral sheath with the femoral vein. The femoral artery and its branches supply most of the thigh as well as the entirety of the leg and foot.
course
Midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the pubic symphysis, the external iliac artery passes under the inguinal ligament into the femoral triangle and becomes the femoral artery. The artery then travels down the anteromedial aspect of the thigh before it passes through the adductor (subsartorial) canal. When the femoral artery passes through the adductor hiatus it becomes the popliteal artery.
Branches
The femoral artery gives off five branches in the femoral triangle and one in the adductor canal, to give six in total. These branches are described below.
Superficial epigastric artery
Superficial epigastric artery (Arteria epigastrica superficialis); Image: Rebecca Betts
Superficial epigastric artery (Arteria epigastrica superficialis)
The superficial epigastric artery arises from the femoral artery, 1 cm distal to the inguinal ligament. It travels through the cribiform fascia and ascends towards the umbilicus within the abdominal superficial fascia. It supplies the skin, superficial fascia and superficial inguinal lymph nodes.
Superficial circumflex iliac artery
The superficial circumflex iliac artery is the smallest branch of the femoral artery. It arises near the superficial epigastric artery. Lateral to the saphenous opening, the artery passes through the fascia lata before coursing towards the anterior superior iliac spine. Like the superficial epigastric artery, it supplies the skin, superficial fascia and superficial inguinal lymph nodes.
Superficial external pudendal artery
The superficial external pudendal artery arises near the superficial epigastric and superficial circumflex iliac arteries. It travels through the cribiform fascia before crossing the spermatic cord deep to the long saphenous vein. It supplies the lower abdominal skin as well as the penile, scrotal or labial skin.
Deep external pudendal artery
The deep external pudendal artery crosses the pectineus and adductor longus muscles before traversing the fascia lata. It supplies the skin of the perineum as well as the skin of the scrotum or labium majus.
Profunda femoris
Deep femoral artery (Arteria profunda femoris); Image: Liene Znotina
Deep femoral artery (Arteria profunda femoris)
Profunda femoris, also known as the deep artery of the thigh is the largest branch of the femoral artery, which arises 3.5 cm distal to the inguinal ligament. The profunda femoris is initially found lateral to the femoral artery before it passes deep to it towards the medial aspect of the femur. It travels between the pectineus and adductor longus muscles before passing between the adductor longus and adductor brevis muscles. It then descends between the adductor longus and adductor magnus muscles before it pierces the adductor magnus to anastamose with the muscular branches of the popliteal artery. The profunda femoris is the main blood supply to the muscles that extend, flex and adduct the thigh.
Descending genicular artery
Descending genicular artery is the most distal branch of the femoral artery, which arises just proximal to the adductor opening within the adductor canal. It descends within the vastus medialis muscle to the medial aspect of the knee. Here, it anastomoses with the medial superior genicular artery. Branches of this artery supply the vastus medialis and adductor magnus muscles as well as the proximomedial skin of the thigh.
Видео Femoral Artery Anatomy | Origin | Branches | Clinical канала Knowing Anatomy
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Femoral artery Anatomy : Origin , Course , Branches and Termination - Animated Lecture
Femoral artery Anatomy : Origin , Course , Branches and Termination - Animated Lecture Internal Iliac Artery (How to remember the branches)
Internal Iliac Artery (How to remember the branches) Anatomy of Celiac trunk / Celiac artery - Origin , Course , Branches , Vascular supply
Anatomy of Celiac trunk / Celiac artery - Origin , Course , Branches , Vascular supply Femoral Nerve Anatomy: Origin, Course, Branches and Clinical application
Femoral Nerve Anatomy: Origin, Course, Branches and Clinical application Femoral Triangle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Femoral Triangle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Sternoclavicular Joint | Synovial Joint | Type | Attachments | Ligaments | clinical
Sternoclavicular Joint | Synovial Joint | Type | Attachments | Ligaments | clinical Adductor canal \ Hunters Canal \ Subsartorial Canal | Boundaries | Contents | Clinical Aspects
Adductor canal \ Hunters Canal \ Subsartorial Canal | Boundaries | Contents | Clinical Aspects Femoral Triangle
Femoral Triangle Femoral triangle anatomy
Femoral triangle anatomy SUPERFICIAL AND DEEP PALMAR ARCH | The White Army
SUPERFICIAL AND DEEP PALMAR ARCH | The White Army Lumbar Plexus - Structure and Branches - Anatomy Tutorial
Lumbar Plexus - Structure and Branches - Anatomy Tutorial Arterial supply of pancreas - Gross anatomy of Abdomen
Arterial supply of pancreas - Gross anatomy of Abdomen Anatomy Front of the thigh ( Adductor Canal ) - Part 7 ( Dr.G.Bhanu Prakash )
Anatomy Front of the thigh ( Adductor Canal ) - Part 7 ( Dr.G.Bhanu Prakash ) Internal Iliac Artery / Hypogastric Artery
Internal Iliac Artery / Hypogastric Artery Femoral Artery and its branches - Anatomy tutorial
Femoral Artery and its branches - Anatomy tutorial ANATOMY OF FEMORAL TRIANGLE , FEMORAL CANAL , FEMORAL SHEATH
ANATOMY OF FEMORAL TRIANGLE , FEMORAL CANAL , FEMORAL SHEATH Medial Femoral Circumflex Artery - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Medial Femoral Circumflex Artery - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim 099 The Branches Of The Axillary Artery
099 The Branches Of The Axillary Artery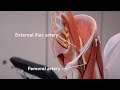 Arteries of the lower limb
Arteries of the lower limb Lower Limb Veins Overview - 3D Anatomy Tutorial
Lower Limb Veins Overview - 3D Anatomy Tutorial