Spine and Leaf network architecture explained | ccna 200-301
#ccna #spine #leaf #freetraining
Many things have changed in the data center over the last decade or so.
In fact, so much has changed that the “old” three-layer model of access, aggregation, and core is no longer ideal.
As This model was designed based on a “south to north” flow of data.
Currently a new architecture is replacing the traditional three-tiered network architecture, which is known as Spine-Leaf architecture
The spine-leaf architecture was developed to overcome the limitations of the three-tier architecture
Given the prevalence of cloud and containerized infrastructure in modern data centers, east-west traffic continues to increase.
Spine-Leaf model is the ideal choice for building the modern data center network.
Spine-Leaf is a two-layer network architecture composed of leaf switches and spine switches.
The leaf layer consists of access switches that connect to devices such as servers or storage devices and WAN devices
Those switches are also called as TOR or EOR switches in modern data centers.
The spine layer is the backbone of the network and is responsible for interconnecting all leaf switches.
In this two-tier Clos architecture, every leaf switch is connected to each of the spine switches in a full-mesh topology.
Leaf-spine network is more useful for data centers that experience more east-west network traffic than north-south traffic.
Advantages of leaf spine architecture
While in a three-tier network, one server may need to traverse a hierarchical path through two aggregation switches and one core switch to communicate with another switch, which adds latency and creates traffic bottlenecks.
With a spine-and-leaf architecture,No matter which leaf switch a server is connected to, it has to cross the same number of devices every time it connects to another server. (The only exception is when the other server is on the same leaf.)
This approach keeps latency at a predictable level and minimizes bottlenecks.because a payload only has to hop to a spine switch and another leaf switch to reach its destination.
Each leaf connects to all spines with no interconnections among neither spines themselves nor leafs which creates a large non-blocking fabric.
Another advantage is the scalability
If oversubscription of a link occurs the process for expanding capacity is straightforward.
An additional spine switch can be added, and uplinks can be extended to every leaf switch, resulting in the addition of interlayer bandwidth and reduction of the oversubscription.
If device port capacity becomes a concern, a new leaf switch can be added by connecting it to every spine switch and adding the network configuration to the switch.
The ease of expansion optimizes the IT department’s process of scaling the network.
If one of the top tier switches were to fail, it would only slightly degrade performance throughout the data center.
Thats all about SPINE-LEAF for today.
In my next session i will discuss about WAN characteristics
Thanks for watching please do like share and subscribe and do not forget to hit the bell icon
Видео Spine and Leaf network architecture explained | ccna 200-301 канала NETWORKING WITH H
Many things have changed in the data center over the last decade or so.
In fact, so much has changed that the “old” three-layer model of access, aggregation, and core is no longer ideal.
As This model was designed based on a “south to north” flow of data.
Currently a new architecture is replacing the traditional three-tiered network architecture, which is known as Spine-Leaf architecture
The spine-leaf architecture was developed to overcome the limitations of the three-tier architecture
Given the prevalence of cloud and containerized infrastructure in modern data centers, east-west traffic continues to increase.
Spine-Leaf model is the ideal choice for building the modern data center network.
Spine-Leaf is a two-layer network architecture composed of leaf switches and spine switches.
The leaf layer consists of access switches that connect to devices such as servers or storage devices and WAN devices
Those switches are also called as TOR or EOR switches in modern data centers.
The spine layer is the backbone of the network and is responsible for interconnecting all leaf switches.
In this two-tier Clos architecture, every leaf switch is connected to each of the spine switches in a full-mesh topology.
Leaf-spine network is more useful for data centers that experience more east-west network traffic than north-south traffic.
Advantages of leaf spine architecture
While in a three-tier network, one server may need to traverse a hierarchical path through two aggregation switches and one core switch to communicate with another switch, which adds latency and creates traffic bottlenecks.
With a spine-and-leaf architecture,No matter which leaf switch a server is connected to, it has to cross the same number of devices every time it connects to another server. (The only exception is when the other server is on the same leaf.)
This approach keeps latency at a predictable level and minimizes bottlenecks.because a payload only has to hop to a spine switch and another leaf switch to reach its destination.
Each leaf connects to all spines with no interconnections among neither spines themselves nor leafs which creates a large non-blocking fabric.
Another advantage is the scalability
If oversubscription of a link occurs the process for expanding capacity is straightforward.
An additional spine switch can be added, and uplinks can be extended to every leaf switch, resulting in the addition of interlayer bandwidth and reduction of the oversubscription.
If device port capacity becomes a concern, a new leaf switch can be added by connecting it to every spine switch and adding the network configuration to the switch.
The ease of expansion optimizes the IT department’s process of scaling the network.
If one of the top tier switches were to fail, it would only slightly degrade performance throughout the data center.
Thats all about SPINE-LEAF for today.
In my next session i will discuss about WAN characteristics
Thanks for watching please do like share and subscribe and do not forget to hit the bell icon
Видео Spine and Leaf network architecture explained | ccna 200-301 канала NETWORKING WITH H
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 4 21 Leaf:Spine Design MSDC
4 21 Leaf:Spine Design MSDC 2 tier | 3 tier | collapsed core network architecture explained | Free CCNA 200-301 |
2 tier | 3 tier | collapsed core network architecture explained | Free CCNA 200-301 | Interface and cable issues |collisions, errors, duplex, speed mismatch| explained |CCNA 200-301
Interface and cable issues |collisions, errors, duplex, speed mismatch| explained |CCNA 200-301 BGP - Complete ENCOR (350-401) Exam Coverage
BGP - Complete ENCOR (350-401) Exam Coverage VxLAN | Part 1 - How VxLAN Works
VxLAN | Part 1 - How VxLAN Works Lunch and Learn - ''Modern Data Center Technologies'' with Arista Networks - phoenixNAP
Lunch and Learn - ''Modern Data Center Technologies'' with Arista Networks - phoenixNAP Data Center NETWORKS (what do they look like??) // FREE CCNA // EP 7
Data Center NETWORKS (what do they look like??) // FREE CCNA // EP 7 Switch | Types of switches | L2 and L3 switch | switch models explained |Free CCNA 200-301|
Switch | Types of switches | L2 and L3 switch | switch models explained |Free CCNA 200-301| How Devices Connect to the Fabric: Understanding Cisco ACI Domains
How Devices Connect to the Fabric: Understanding Cisco ACI Domains What is VLAN and Why VLAN?
What is VLAN and Why VLAN?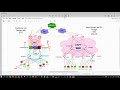 Spine Leaf Data Center architecture and design compared to traditional design
Spine Leaf Data Center architecture and design compared to traditional design TCP vs UDP Comparison | Cisco CCNA 200-301
TCP vs UDP Comparison | Cisco CCNA 200-301 Wireless principles : wlan topologies | repeater , workgroup & outdoor bridge | ccna 200-301
Wireless principles : wlan topologies | repeater , workgroup & outdoor bridge | ccna 200-301 Comprendre l'ARCHITECTURE d'un DATA CENTER "CCNA FAST FREE DAY 12"
Comprendre l'ARCHITECTURE d'un DATA CENTER "CCNA FAST FREE DAY 12" How VXLAN Works Example
How VXLAN Works Example VxLAN | Part 3 - Spine Leaf Topology
VxLAN | Part 3 - Spine Leaf Topology Webinar: Networking Design and Best Practices
Webinar: Networking Design and Best Practices Traceroute (tracert) Explained - Network Troubleshooting
Traceroute (tracert) Explained - Network Troubleshooting Syslog Explained | Cisco CCNA 200-301
Syslog Explained | Cisco CCNA 200-301 IP address : Public and Private IP address explained | CCNA 200-301
IP address : Public and Private IP address explained | CCNA 200-301