Anatomy Of The Knee - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the anatomy of the knee joint.
•Femur
•Tibia
•Fibula
•Patella
•Joint capsule: articular surface of the femur and articular surface of the patella.
•Femoral condyles
•Meniscus
•Anterior cruciate ligament
•Posterior cruciate ligament
•Medial collateral ligament
•Lateral collateral ligament
•Quadriceps muscle attached to the patella
•Patellar tendon
•Hamstrings muscle at the back of the knee
Several bursae are seen around the knees
•Suprapatellar bursa
•Prepatellar bursa
•Infrapatellar bursa
•Pes anserine bursa
These bursae allow the knee cap to slide freely underneath the skin while bending and straightening the knee.
The area of depression located at the back of the knee is called the popliteal fossa.
Posterior view of the knee
Posterior cruciate ligament
Muscles:
•popliteus
•Plantaris
•Soleus
•Biceps femoris
•Semitendinosus
•Semimembranosus
•Gastrocnemius
Popliteal fossa: neurovascular bundle in the fossa
•Popliteal artery and vein
•Tibial nerve
•Common peroneal nerve
Both the tibial and the common peroneal nerves arise from the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve travels down the thigh to the area of the popliteal fossa and at this point it divides into the tibial and common peroneal nerves.
The popliteal fossa is a closely packed space. It is bounded by the biceps femoris laterally as well as the semitendinosus and the semimembranosus medially. The lower part of the space is formed by the two head of the gastrocnemius muscle.
On the medial side of the knee, you can find the arrangement of the tendons inserted in the tibia and the medial collateral ligament.
On the medial side of the knee you can see the biceps femoris tendon and the iliotibial band. You can also see the lateral collateral ligament.
The articular cartilage of the knee is different from the meniscus. it is worn out by aging and wear and tear. This condition is called osteoarthritis. The hyaline cartilage becomes roughened and bumpy.
Injuries around the knee
The quadriceps tendon, the patellar tendon and the patella cause active extension of the knee. Any disruption, the patient will be unable to actively extend the knee.
In anterior cruciate ligament injury the tibia moves forward. In a posterior cruciate ligament injury the tibia moves backward.
Rupture of the collateral ligament of the knee, lateral or medial, will cause abnormal side movement of the leg.
Inside the knee between the femur and the tibia you will see the meniscus. healing of meniscal tear is good at the periphery because of good blood supply.
Become a friend on facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Видео Anatomy Of The Knee - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
•Femur
•Tibia
•Fibula
•Patella
•Joint capsule: articular surface of the femur and articular surface of the patella.
•Femoral condyles
•Meniscus
•Anterior cruciate ligament
•Posterior cruciate ligament
•Medial collateral ligament
•Lateral collateral ligament
•Quadriceps muscle attached to the patella
•Patellar tendon
•Hamstrings muscle at the back of the knee
Several bursae are seen around the knees
•Suprapatellar bursa
•Prepatellar bursa
•Infrapatellar bursa
•Pes anserine bursa
These bursae allow the knee cap to slide freely underneath the skin while bending and straightening the knee.
The area of depression located at the back of the knee is called the popliteal fossa.
Posterior view of the knee
Posterior cruciate ligament
Muscles:
•popliteus
•Plantaris
•Soleus
•Biceps femoris
•Semitendinosus
•Semimembranosus
•Gastrocnemius
Popliteal fossa: neurovascular bundle in the fossa
•Popliteal artery and vein
•Tibial nerve
•Common peroneal nerve
Both the tibial and the common peroneal nerves arise from the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve travels down the thigh to the area of the popliteal fossa and at this point it divides into the tibial and common peroneal nerves.
The popliteal fossa is a closely packed space. It is bounded by the biceps femoris laterally as well as the semitendinosus and the semimembranosus medially. The lower part of the space is formed by the two head of the gastrocnemius muscle.
On the medial side of the knee, you can find the arrangement of the tendons inserted in the tibia and the medial collateral ligament.
On the medial side of the knee you can see the biceps femoris tendon and the iliotibial band. You can also see the lateral collateral ligament.
The articular cartilage of the knee is different from the meniscus. it is worn out by aging and wear and tear. This condition is called osteoarthritis. The hyaline cartilage becomes roughened and bumpy.
Injuries around the knee
The quadriceps tendon, the patellar tendon and the patella cause active extension of the knee. Any disruption, the patient will be unable to actively extend the knee.
In anterior cruciate ligament injury the tibia moves forward. In a posterior cruciate ligament injury the tibia moves backward.
Rupture of the collateral ligament of the knee, lateral or medial, will cause abnormal side movement of the leg.
Inside the knee between the femur and the tibia you will see the meniscus. healing of meniscal tear is good at the periphery because of good blood supply.
Become a friend on facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Видео Anatomy Of The Knee - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Anatomy Of The Thigh - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Anatomy Of The Thigh - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim How to Tell if Knee Pain is Meniscus or Ligament Injury
How to Tell if Knee Pain is Meniscus or Ligament Injury Knee Dislocation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Knee Dislocation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Knee Examination Inspection & Palpation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Knee Examination Inspection & Palpation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim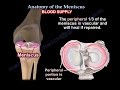 Anatomy Of The Meniscus - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Anatomy Of The Meniscus - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Clinical Anatomy - Knee
Clinical Anatomy - Knee Tests For Examination Of The Knee - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Tests For Examination Of The Knee - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Is Your Knee Pain Coming From a Meniscus Tear or Ligament Strain/Tear? How to Tell.
Is Your Knee Pain Coming From a Meniscus Tear or Ligament Strain/Tear? How to Tell. Musculoskeletal Physical Exam: Knee
Musculoskeletal Physical Exam: Knee Anatomy of the Knee Joint
Anatomy of the Knee Joint Anatomy of Movement Of The Hip - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Anatomy of Movement Of The Hip - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim LIGAMENTS OF THE KNEE
LIGAMENTS OF THE KNEE Knee Anatomy Animated Tutorial
Knee Anatomy Animated Tutorial Anatomy Of The Lower Leg - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Anatomy Of The Lower Leg - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Lisfranc Injury - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Lisfranc Injury - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Muscles that move knee
Muscles that move knee Knee injury ,Injuries - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Knee injury ,Injuries - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Knee bones and ligaments
Knee bones and ligaments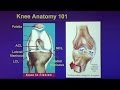 Common Traumatic Knee Injuries: Oh My Aching Knee
Common Traumatic Knee Injuries: Oh My Aching Knee Clinical Anatomy - Knee mensicus and knee joint
Clinical Anatomy - Knee mensicus and knee joint