Python – Finding the Middle of a Linked List: Two Approaches (DSA) 🚀 #PythonDSA #CodingInterview
The Finding the Middle of a Linked List problem requires identifying the middle node in a singly linked list. This task is fundamental in various applications, such as splitting a linked list into two halves or optimizing certain operations.
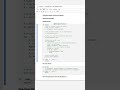
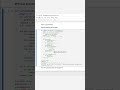
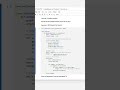
Method 1 – Two-Pointer (Tortoise and Hare) Approach:
How It Works:
Utilize two pointers, slow and fast.
slow moves one step at a time, while fast moves two steps.
When fast reaches the end, slow will be at the middle node.
Efficiency:
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Advantages:
Efficient and requires only a single traversal.
Does not need prior knowledge of the list's length.
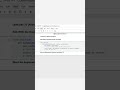
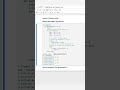
Method 2 – Counting Nodes Approach:
How It Works:
Traverse the list to count the total number of nodes.
Calculate the middle index as count // 2.
Traverse the list again to the middle index.
Efficiency:
Time Complexity: O(n) (two traversals)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Advantages:
Simple to implement.
Disadvantages:
Requires two traversals of the list.
Less efficient compared to the two-pointer approach.
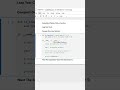
Why Is This Problem Important?
Interview Relevance:
Commonly asked in technical interviews to assess understanding of linked list manipulations.
Real-World Applications:
Useful in scenarios where operations on the middle element are required, such as in certain sorting algorithms or data processing tasks.
Learning Benefit:
Enhances understanding of pointer manipulation and traversal techniques in linked lists.
#Python #DSA #LinkedList #CodingInterview #Algorithms #PythonForBeginners #PythonTips #Leetcode #CompetitiveProgramming #PythonShorts #SoftwareEngineering #LearnPython
Видео Python – Finding the Middle of a Linked List: Two Approaches (DSA) 🚀 #PythonDSA #CodingInterview канала CodeVisium
Method 1 – Two-Pointer (Tortoise and Hare) Approach:
How It Works:
Utilize two pointers, slow and fast.
slow moves one step at a time, while fast moves two steps.
When fast reaches the end, slow will be at the middle node.
Efficiency:
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Advantages:
Efficient and requires only a single traversal.
Does not need prior knowledge of the list's length.
Method 2 – Counting Nodes Approach:
How It Works:
Traverse the list to count the total number of nodes.
Calculate the middle index as count // 2.
Traverse the list again to the middle index.
Efficiency:
Time Complexity: O(n) (two traversals)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Advantages:
Simple to implement.
Disadvantages:
Requires two traversals of the list.
Less efficient compared to the two-pointer approach.
Why Is This Problem Important?
Interview Relevance:
Commonly asked in technical interviews to assess understanding of linked list manipulations.
Real-World Applications:
Useful in scenarios where operations on the middle element are required, such as in certain sorting algorithms or data processing tasks.
Learning Benefit:
Enhances understanding of pointer manipulation and traversal techniques in linked lists.
#Python #DSA #LinkedList #CodingInterview #Algorithms #PythonForBeginners #PythonTips #Leetcode #CompetitiveProgramming #PythonShorts #SoftwareEngineering #LearnPython
Видео Python – Finding the Middle of a Linked List: Two Approaches (DSA) 🚀 #PythonDSA #CodingInterview канала CodeVisium
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
16 марта 2025 г. 11:56:09
00:00:11
Другие видео канала