Fracture Healing, Bridge Plate - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes bridge plating in orthopaedic fractures.
There are many types of orthopedic plates. The indication and the function for each plate could be different.
Bridge plate is one of the plates used in orthopedics. The technique is what gives the plate its name.
A bridge plate is used wen the fracture has multiple fragments or comminution.
The bridge will bypass the comminution.
The plate is fixed to the two main fragments- the proximal and distal. This leaves the fracture zone untouched and undisturbed. The fracture zone is not exposed.
The bridge respects the biology of the fracture and the soft tissue. It preserves the vascularity of the fracture, which will help with healing and reduce complications.
There is no need for anatomic reduction- the bridge plate acts as an extramedullary splint.
One incisions can be used (but do not touch the middle segment that is comminuted) or two incisions (on proximal and one distal) can be used.
Sometimes minimally invasive incisions are used. I use two incisions, one proximal and one distal, and leave the comminated area undisturbed.
One of the best advances in orthopedics is increased awareness about the value of soft tissue. Try to protect the soft tissue around the bone, minimal periosteal stripping, and minimal dissection of the soft tissue around the fracture. This is usually accomplished with bridge plate placement and sub-muscular fixation.
Preserve the blood supply.
Maintain the length, rotation, and axial alignment.
The percutaneous locking plates may have a higher chance of malunion.
Usually use indirect reduction techniques, either manual traction or, less commonly, distractors.
The plate will provide the fracture with relative stability.
The plate is usually long. The span segment is longer than a standard compression plate so the force is distributed over a larger distance.The strain on the plate will be lower with a higher resistance to fatigue.
Fracture healing will be done by secondary callus or secondary bone healing.
Stages of secondary bone healing:
-Hematoma
-Inflammation
-Soft callus (type II collagen). The transforming growth factor (beta-1) will make the mesenchymal cell produce type II collagen and proteoglycans, trying to produce endochondral ossification.
-Hard callus (Type I collagen- stimulated by insulin-like growth factor 2)
-Remodeling (esp. in children)
If the fracture s simple, then you do not need this technique. Anatomic reduction will be done and absolute stability will be obtained with a shorter plate, which will give you primary bone healing with osteonal remodeling.
What screws do you use?
-Locking screws provide axial and angulation stability
-It is better to use a locking compression plate, which allows insertion of standard screws and locking screws. The rigidity of the plate decreases as the distance between the inner most screws increases.
-Regular screws allow approximation of the plate to the bone and the relative stability of this plate will not require precise contouring when locking screws are used.
-The screws closest tot he fracture see the most stress
-Better to use bicortical locking screws because they have better resistance to torsion than unicortical screws.
Pre-operative planning will be necessary.
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Видео Fracture Healing, Bridge Plate - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
There are many types of orthopedic plates. The indication and the function for each plate could be different.
Bridge plate is one of the plates used in orthopedics. The technique is what gives the plate its name.
A bridge plate is used wen the fracture has multiple fragments or comminution.
The bridge will bypass the comminution.
The plate is fixed to the two main fragments- the proximal and distal. This leaves the fracture zone untouched and undisturbed. The fracture zone is not exposed.
The bridge respects the biology of the fracture and the soft tissue. It preserves the vascularity of the fracture, which will help with healing and reduce complications.
There is no need for anatomic reduction- the bridge plate acts as an extramedullary splint.
One incisions can be used (but do not touch the middle segment that is comminuted) or two incisions (on proximal and one distal) can be used.
Sometimes minimally invasive incisions are used. I use two incisions, one proximal and one distal, and leave the comminated area undisturbed.
One of the best advances in orthopedics is increased awareness about the value of soft tissue. Try to protect the soft tissue around the bone, minimal periosteal stripping, and minimal dissection of the soft tissue around the fracture. This is usually accomplished with bridge plate placement and sub-muscular fixation.
Preserve the blood supply.
Maintain the length, rotation, and axial alignment.
The percutaneous locking plates may have a higher chance of malunion.
Usually use indirect reduction techniques, either manual traction or, less commonly, distractors.
The plate will provide the fracture with relative stability.
The plate is usually long. The span segment is longer than a standard compression plate so the force is distributed over a larger distance.The strain on the plate will be lower with a higher resistance to fatigue.
Fracture healing will be done by secondary callus or secondary bone healing.
Stages of secondary bone healing:
-Hematoma
-Inflammation
-Soft callus (type II collagen). The transforming growth factor (beta-1) will make the mesenchymal cell produce type II collagen and proteoglycans, trying to produce endochondral ossification.
-Hard callus (Type I collagen- stimulated by insulin-like growth factor 2)
-Remodeling (esp. in children)
If the fracture s simple, then you do not need this technique. Anatomic reduction will be done and absolute stability will be obtained with a shorter plate, which will give you primary bone healing with osteonal remodeling.
What screws do you use?
-Locking screws provide axial and angulation stability
-It is better to use a locking compression plate, which allows insertion of standard screws and locking screws. The rigidity of the plate decreases as the distance between the inner most screws increases.
-Regular screws allow approximation of the plate to the bone and the relative stability of this plate will not require precise contouring when locking screws are used.
-The screws closest tot he fracture see the most stress
-Better to use bicortical locking screws because they have better resistance to torsion than unicortical screws.
Pre-operative planning will be necessary.
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Видео Fracture Healing, Bridge Plate - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Bone Healing, Buttress Plate - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Bone Healing, Buttress Plate - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim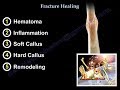 Fracture Healing - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Fracture Healing - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Need Desire & Problems of Orthopedic Surgeons With Respect to Implant Companies
Need Desire & Problems of Orthopedic Surgeons With Respect to Implant Companies Frozen Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Frozen Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Proximal Humerus Fracture
Proximal Humerus Fracture The principle of the internal fixator using the Locking Compression Plate (LCP) - AO Trauma
The principle of the internal fixator using the Locking Compression Plate (LCP) - AO Trauma Sciatica Clinical Diagnosis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Sciatica Clinical Diagnosis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Calcific Tendonitis of the shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Calcific Tendonitis of the shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Fracture Healing | ANIMATION | BASICS | The Young Orthopod
Fracture Healing | ANIMATION | BASICS | The Young Orthopod Principles of Fracture Fixation | Orthopedic Basics
Principles of Fracture Fixation | Orthopedic Basics Carpal Tunnel Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Guyan's Canal Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Guyan's Canal Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Osteonecrosis Of The Hip Stages & Treatment - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil
Osteonecrosis Of The Hip Stages & Treatment - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Galeazzi Fracture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Galeazzi Fracture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Anatomy of a Fracture as a Result of Systemic Bone Loss
Anatomy of a Fracture as a Result of Systemic Bone Loss Knee Pain & Arthritis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Knee Pain & Arthritis - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Basics of Osteotomy
Basics of Osteotomy Nonunion of the Humerus - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Nonunion of the Humerus - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim How does a plate and screws help a broken bone heal?
How does a plate and screws help a broken bone heal? Quadriga Effect and the RMO
Quadriga Effect and the RMO