Gout and Pseudogout, Joint Pain- Everything You Need To Know- Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Educational video describing the condition of gout and pseudogout.
The most common joint affected by gout is the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint. The most common joint affected by pseudogout is the knee joint. Gout and pseudogout are similar problems with different causes.
Gout
Gout is caused by the build-up of uric acid crystals inside a joint. The best test to diagnose gout is with a joint fluid analysis. Elevated uric acid is not a good criterion. 90% of patients suffering from gout are men between the ages of 40-60 years.
Gout crystals are needle-shaped and negatively birefringent. When placed under polarized light they will be yellow.
Uric acid builds up in the body by two main mechanisms:
1-Excessive urate production.
2-Diminished urate clearance.
Uric acid is produced from the breakdown of proteins inside the body and from the proteins of food that is eaten.
Precipitating factors
The sudden attack of gout can be brought on by anything that increases the level of uric acid in the blood such as:
•Dehydration
•Increased consumption of alcohol
•Eating large amount of meat or seafood
•Trauma/surgery
Diagnostic testing
•Aspiration and analysis of the joint fluid is the best method for diagnosis.
•There are blood tests such as white blood cell count, C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and uric acid level that are helpful in supporting the diagnosis if elevated, but if normal cannot definitively rule out gout or pseudogout.
Pseudogout
Pseudogout is a metabolic disease where calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals (CPPD) are formed within the joint space. Most often affects the knee, occurs more in older patients. Calcification of fibrocartilage (chondrocalcinosis).
Pseudogout crystals are rhomboid shaped and positively birefringent. Crystals will be blue when placed under polarized light.
Associated conditions:
•Hyperparathyroidism
•Rheumatoid arthritis
•Gout
Gout and pseudogout both show a sudden onset of pain, redness and swelling typically affecting a single joint in 80% of the cases.
Gout symptoms and signs include pain, swelling and arthritis. Patients with gout have periarticular erosions along with the formation of uric acid soft tissue masses in and around the joint which can be seen on x-ray. Soft tissue tophus deposition with periarticular erosions call “punch-out” lesions.
X-rays in pseudogout will show thin calcification in the articular cartilage or menisci, with involvement of the patellofemoral joint. Calcifications of the synovium, tendon and ligaments can also be seen.
Treatment of Gout & pseudogout
•Acute gout: indocine, colchicine (be aware of peptic ulcer)
•Chronic gout: allopurinol (xanthine oxidase inhibitor), colchicine
•Uricosuric drugs such as probenecid which increase uric acid excretion by the kidneys may be helpful.
•Treatment of pseudogout: NSAIDs, intraarticular injections.
Become a friend on facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
The contents of this video (and logo) are the intellectual property of and were created by Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. The music was provided by a free download.
Видео Gout and Pseudogout, Joint Pain- Everything You Need To Know- Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
The most common joint affected by gout is the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint. The most common joint affected by pseudogout is the knee joint. Gout and pseudogout are similar problems with different causes.
Gout
Gout is caused by the build-up of uric acid crystals inside a joint. The best test to diagnose gout is with a joint fluid analysis. Elevated uric acid is not a good criterion. 90% of patients suffering from gout are men between the ages of 40-60 years.
Gout crystals are needle-shaped and negatively birefringent. When placed under polarized light they will be yellow.
Uric acid builds up in the body by two main mechanisms:
1-Excessive urate production.
2-Diminished urate clearance.
Uric acid is produced from the breakdown of proteins inside the body and from the proteins of food that is eaten.
Precipitating factors
The sudden attack of gout can be brought on by anything that increases the level of uric acid in the blood such as:
•Dehydration
•Increased consumption of alcohol
•Eating large amount of meat or seafood
•Trauma/surgery
Diagnostic testing
•Aspiration and analysis of the joint fluid is the best method for diagnosis.
•There are blood tests such as white blood cell count, C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and uric acid level that are helpful in supporting the diagnosis if elevated, but if normal cannot definitively rule out gout or pseudogout.
Pseudogout
Pseudogout is a metabolic disease where calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals (CPPD) are formed within the joint space. Most often affects the knee, occurs more in older patients. Calcification of fibrocartilage (chondrocalcinosis).
Pseudogout crystals are rhomboid shaped and positively birefringent. Crystals will be blue when placed under polarized light.
Associated conditions:
•Hyperparathyroidism
•Rheumatoid arthritis
•Gout
Gout and pseudogout both show a sudden onset of pain, redness and swelling typically affecting a single joint in 80% of the cases.
Gout symptoms and signs include pain, swelling and arthritis. Patients with gout have periarticular erosions along with the formation of uric acid soft tissue masses in and around the joint which can be seen on x-ray. Soft tissue tophus deposition with periarticular erosions call “punch-out” lesions.
X-rays in pseudogout will show thin calcification in the articular cartilage or menisci, with involvement of the patellofemoral joint. Calcifications of the synovium, tendon and ligaments can also be seen.
Treatment of Gout & pseudogout
•Acute gout: indocine, colchicine (be aware of peptic ulcer)
•Chronic gout: allopurinol (xanthine oxidase inhibitor), colchicine
•Uricosuric drugs such as probenecid which increase uric acid excretion by the kidneys may be helpful.
•Treatment of pseudogout: NSAIDs, intraarticular injections.
Become a friend on facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
The contents of this video (and logo) are the intellectual property of and were created by Dr. Nabil Ebraheim. The music was provided by a free download.
Видео Gout and Pseudogout, Joint Pain- Everything You Need To Know- Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Knee Pain, Pseudogout, and Vitamin K2 Benefits – Prevent Gout with Vitamin K2 – Dr.Berg
Knee Pain, Pseudogout, and Vitamin K2 Benefits – Prevent Gout with Vitamin K2 – Dr.Berg Pseudogout | Pathophysiology, Symptoms and Treatment
Pseudogout | Pathophysiology, Symptoms and Treatment Pseudogout
Pseudogout Why is My Knee Swollen
Why is My Knee Swollen Gout , Pseudogout & Joint Pain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Gout , Pseudogout & Joint Pain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Gout | Causes, Pathophysiology, Risk Factors (ex. Diet), Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Gout | Causes, Pathophysiology, Risk Factors (ex. Diet), Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment What Happens During a Gout Attack | WebMD
What Happens During a Gout Attack | WebMD Anatomy of the Elbow - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Anatomy of the Elbow - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim How I mix my colors and its super easy 🎨 👩🎤 | 403 Color recipes for Beginners | TheArtSherpa
How I mix my colors and its super easy 🎨 👩🎤 | 403 Color recipes for Beginners | TheArtSherpa Gout VS Pseudogout
Gout VS Pseudogout Gout and pseudogout | Muscular-skeletal diseases | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
Gout and pseudogout | Muscular-skeletal diseases | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy How to Get Rid of Arthritic Knee Pain in 30 SECONDS
How to Get Rid of Arthritic Knee Pain in 30 SECONDS Achilles Tendon Rupture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Achilles Tendon Rupture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Gout - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
Gout - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology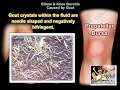 Elbow & Knee Bursitis Caused By Gout - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Elbow & Knee Bursitis Caused By Gout - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Best & Worst Foods to Eat with Gout | Reduce Risk of Gout Attacks and Hyperuricemia
Best & Worst Foods to Eat with Gout | Reduce Risk of Gout Attacks and Hyperuricemia Cubital Tunnel Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim The Gout Diet and the Importance of Eating the Right Foods (3 of 6)
The Gout Diet and the Importance of Eating the Right Foods (3 of 6) Shoulder Dislocation Anatomy - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Shoulder Dislocation Anatomy - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim