Coarctation of the aorta (CoA)
Coarctation of the aorta is a congenital (present at birth) heart defect involving a narrowing of the aorta.
The aorta is the large artery that carries oxygen-rich (red) blood from the left ventricle to the body. It is shaped like a candy cane. The first section moves up towards the head (ascending aorta), then curves in a C-shape as smaller arteries that are attached to it carry blood to the head and arms (aortic arch). After the curve, the aorta becomes straight again, and moves downward towards the abdomen, carrying blood to the lower part of the body (descending aorta).
The narrowed segment called coarctation can occur anywhere in the aorta, but is most likely to happen in the segment just after the aortic arch. This narrowing restricts the amount of oxygen-rich (red) blood that can travel to the lower part of the body. Varying degrees of narrowing can occur.
The more severe the narrowing, the more symptomatic a child will be, and the earlier the problem will be noticed. In some cases, coarctation is noted in infancy. In others, however, it may not be noted until school-age or adolescence.
About one-half of children with coarctation of the aorta also have a bicuspid aortic valve—a valve that has 2 leaflets instead of the usual 3.
Coarctation of the aorta occurs in a small percentage of children with congenital heart disease. Boys have the defect more commonly than girls do.
Видео Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) канала D Seetaram
The aorta is the large artery that carries oxygen-rich (red) blood from the left ventricle to the body. It is shaped like a candy cane. The first section moves up towards the head (ascending aorta), then curves in a C-shape as smaller arteries that are attached to it carry blood to the head and arms (aortic arch). After the curve, the aorta becomes straight again, and moves downward towards the abdomen, carrying blood to the lower part of the body (descending aorta).
The narrowed segment called coarctation can occur anywhere in the aorta, but is most likely to happen in the segment just after the aortic arch. This narrowing restricts the amount of oxygen-rich (red) blood that can travel to the lower part of the body. Varying degrees of narrowing can occur.
The more severe the narrowing, the more symptomatic a child will be, and the earlier the problem will be noticed. In some cases, coarctation is noted in infancy. In others, however, it may not be noted until school-age or adolescence.
About one-half of children with coarctation of the aorta also have a bicuspid aortic valve—a valve that has 2 leaflets instead of the usual 3.
Coarctation of the aorta occurs in a small percentage of children with congenital heart disease. Boys have the defect more commonly than girls do.
Видео Coarctation of the aorta (CoA) канала D Seetaram
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Coarctation of the Aorta
Coarctation of the Aorta Aortic Valve Disease, Animation
Aortic Valve Disease, Animation Texas Children's Heart Surgery for Aortic Coarctation: Luke's story
Texas Children's Heart Surgery for Aortic Coarctation: Luke's story Blood Flow through the Heart in 2 MINUTES
Blood Flow through the Heart in 2 MINUTES Preventing developmental delays in babies after heart surgery
Preventing developmental delays in babies after heart surgery Tetralogy of Fallot | Cincinnati Children's
Tetralogy of Fallot | Cincinnati Children's Coarctation of the Aorta Nursing Pediatrics | Congenital Heart Disease Defects
Coarctation of the Aorta Nursing Pediatrics | Congenital Heart Disease Defects Single Ventricle Malformations - The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (1 of 6)
Single Ventricle Malformations - The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (1 of 6) Aortic Valve Replacement
Aortic Valve Replacement Transposition of the Great Arteries
Transposition of the Great Arteries Coarctation of aorta (Infantile type vs adult type) mnemonic
Coarctation of aorta (Infantile type vs adult type) mnemonic 215 - Infantile and adult-type coarctation of Aorta - USMLE STEP 1 USMLE ACE
215 - Infantile and adult-type coarctation of Aorta - USMLE STEP 1 USMLE ACE Aorta Ultrasound - Introduction - SonoSite, Inc.
Aorta Ultrasound - Introduction - SonoSite, Inc. Retrograde Transpedal Artery Access for Limb Ischemia (Cardiology Team , AIIMS , BHUBANESWAR)
Retrograde Transpedal Artery Access for Limb Ischemia (Cardiology Team , AIIMS , BHUBANESWAR) Coarctation of the Aorta
Coarctation of the Aorta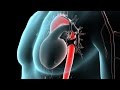 Anatomy of the Aorta
Anatomy of the Aorta Bubble contrast echocardiography
Bubble contrast echocardiography Coarctation of the Aorta CoA repair, causes, symptoms & pathology
Coarctation of the Aorta CoA repair, causes, symptoms & pathology Einsenmenger coarctation of aorta | Circulatory System and Disease | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
Einsenmenger coarctation of aorta | Circulatory System and Disease | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy PDA - ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY SERIES BY DR ANKUR K CHAUDHARI
PDA - ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY SERIES BY DR ANKUR K CHAUDHARI