Shoulder Examination / Subacromial, Cuff - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the clinical evaluation tests for Shoulder and Rotator Cuff injuries.
Neer’s test
•Position of the patient: patient is standing or sitting upright.
•Performing the tets: the examiner will passively elevate the pronated arm of the patient above the level of the shoulder.
•Positive finding: pain at the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder indicates subacromial impingement.
Hawkin’s test
•position of the patient: patient is standing or sitting upright with the arm fully adducted and forwardly flexed. The elbow is also flexed.
•performing the test: the examiner will place one hand on the patient’s shoulder and apply internal rotation to the affected arm with the other hand.
•positive findings: pain at the shoulder indicates subacromial impingement.
Drop arm test:
•position of the patient: patient is standing or sitting upright.
•performing the test: the patient is asked to hold the affected arm in abduction at the level of the shoulder then smoothly adduct the arm.
•positive findings: a patient who is suffering from a rotator cuff tear can lower the arm smoothly to the side. A patient suffering from a rotator cuff tear will not be able to hold the arm in abduction and the arm will drop rapidly.
Belly press test
•position of the patient: patient is standing with the hand of the affected arm at rest against the stomach with the elbow anterior to the midaxillary line.
•performing the test: the patient is then asked to press the belly using the affected arm without moving the elbow.
•positive findings: failure to maintain the elbow anterior to the midaxillary line while pressing against the belly indicates predominantly an infrapsinatus tendon tear.
Lift off test
•position of the patient: patient is standing with affected arm internally rotated behind the back so that the dorsum of the hand will be resting on the lumbar area.
•performing the test: the examiner will passively lift the arm away from the patient’s back.
•positive findings: once the examiner releases the arm, failure to maintain the position of the arm away from the back indicates a subscapularis tendon tear.
Adduction/external rotation test
•position of the patient: patient is standing with the affected arm adducted (slightly abducted) and elbow flexed.
•performing the test: the examiner will fully externally rotate the arm.
•positive findings: with the release of the arm, failure to maintain active full external rotation indicates a supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendon tear.
Jobe test
•position of the patient: patient is standing or sitting upright. The arm should be anteriorly flexed at the level of the shoulder. Fully pronate the arm into “empty can position”
•performing the test: the patient should resist the downward force applied on the forearm by the examiner.
•positive findings: pain or weakness indicates a supraspinatus tendon lesion.
Become a friend on facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Видео Shoulder Examination / Subacromial, Cuff - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Neer’s test
•Position of the patient: patient is standing or sitting upright.
•Performing the tets: the examiner will passively elevate the pronated arm of the patient above the level of the shoulder.
•Positive finding: pain at the anterolateral aspect of the shoulder indicates subacromial impingement.
Hawkin’s test
•position of the patient: patient is standing or sitting upright with the arm fully adducted and forwardly flexed. The elbow is also flexed.
•performing the test: the examiner will place one hand on the patient’s shoulder and apply internal rotation to the affected arm with the other hand.
•positive findings: pain at the shoulder indicates subacromial impingement.
Drop arm test:
•position of the patient: patient is standing or sitting upright.
•performing the test: the patient is asked to hold the affected arm in abduction at the level of the shoulder then smoothly adduct the arm.
•positive findings: a patient who is suffering from a rotator cuff tear can lower the arm smoothly to the side. A patient suffering from a rotator cuff tear will not be able to hold the arm in abduction and the arm will drop rapidly.
Belly press test
•position of the patient: patient is standing with the hand of the affected arm at rest against the stomach with the elbow anterior to the midaxillary line.
•performing the test: the patient is then asked to press the belly using the affected arm without moving the elbow.
•positive findings: failure to maintain the elbow anterior to the midaxillary line while pressing against the belly indicates predominantly an infrapsinatus tendon tear.
Lift off test
•position of the patient: patient is standing with affected arm internally rotated behind the back so that the dorsum of the hand will be resting on the lumbar area.
•performing the test: the examiner will passively lift the arm away from the patient’s back.
•positive findings: once the examiner releases the arm, failure to maintain the position of the arm away from the back indicates a subscapularis tendon tear.
Adduction/external rotation test
•position of the patient: patient is standing with the affected arm adducted (slightly abducted) and elbow flexed.
•performing the test: the examiner will fully externally rotate the arm.
•positive findings: with the release of the arm, failure to maintain active full external rotation indicates a supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendon tear.
Jobe test
•position of the patient: patient is standing or sitting upright. The arm should be anteriorly flexed at the level of the shoulder. Fully pronate the arm into “empty can position”
•performing the test: the patient should resist the downward force applied on the forearm by the examiner.
•positive findings: pain or weakness indicates a supraspinatus tendon lesion.
Become a friend on facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Видео Shoulder Examination / Subacromial, Cuff - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 The Exam for Shoulder Pain - Stanford Medicine 25
The Exam for Shoulder Pain - Stanford Medicine 25 Shoulder Examination - Orthopaedics
Shoulder Examination - Orthopaedics Shoulder Impingement - Dr. Richard Hawkins
Shoulder Impingement - Dr. Richard Hawkins Rotator Cuff Muscles - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Rotator Cuff Muscles - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Painful Arc Syndrome | Shoulder Impingement
Painful Arc Syndrome | Shoulder Impingement Cervical Spine Nerve Root Exam - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Cervical Spine Nerve Root Exam - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Shoulder Exam - Dr. Hawkins
Shoulder Exam - Dr. Hawkins The Essential Shoulder Exam - Brian Feeley, MD
The Essential Shoulder Exam - Brian Feeley, MD What is Causing Your Shoulder Pain? Tests You Can Do Yourself.
What is Causing Your Shoulder Pain? Tests You Can Do Yourself. Lesions Of The Shoulder SLAP Tear - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Lesions Of The Shoulder SLAP Tear - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Tests For Examination Of The Knee - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Tests For Examination Of The Knee - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Neurological Evaluation Of The Lumbar Nerve Roots - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Neurological Evaluation Of The Lumbar Nerve Roots - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Rotator Cuff Muscle Examination - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Rotator Cuff Muscle Examination - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Shoulder Full Assessment Run Through | Clinical Physio Premium
Shoulder Full Assessment Run Through | Clinical Physio Premium Shoulder dislocation , Hill Sachs Lesion - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Shoulder dislocation , Hill Sachs Lesion - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Absolute Best Shoulder Impingement Exercises (Self-Treatments)
Absolute Best Shoulder Impingement Exercises (Self-Treatments) Thoracic Outlet Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim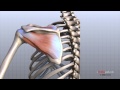 Shoulder Anatomy Animated Tutorial
Shoulder Anatomy Animated Tutorial Is Your Shoulder Pain an Impingement? 4 Quick Tests You Can Try.
Is Your Shoulder Pain an Impingement? 4 Quick Tests You Can Try. Shoulder Examination Inspection & Palpation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Shoulder Examination Inspection & Palpation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim