Femur fracture ,Subtrochanteric fracture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes proximal femur subtrochanteric fractures and fixation.
About 10% of all fractures in the proximal femur. Fracture between the lesser trochanter and a point 5 cm distal to the lesser trochanter. The subtrochanteric region is the worst area on the femur for fracture to occur. There is high compression and tensile forces in this area. Less vascularity, less healing potential and ability. This area is made of hard cortical bone that does not heal well. There is a lot of deforming forces on the proximal fragment. The subtrochanteric fracture is flexed by the iliopsoas muscle, abducted by the gluteus medius and minimus muscles, and externally rotated by the short rotator muscles. There is a high risk of implant failure. Need bone to bone transfer in this area, especially if you are going to open the fracture.
Atypical fracture is associated with bisphosphonate use, there will be thigh pain. The fracture may be seen on an MRI and usually there is no history of trauma. Using bisphosphonate for a long period of time may cause this atypical subtrochanteric fracture of the femur. The fracture may appear as a localized thickening on the lateral side of the femur. The fracture is caused by bending forces. When you bend a bone, there will be two parts: tension component (transverse component will be on the lateral side) and the compression component (oblique “spike” on the medial side: no comminution).
Typical fracture occurs due to high energy trauma such as car accidents or from a fall.
In the majority of subtrochanteric fractures, either typical or atypical, we will use a rod. Because the rod is inside the bone, and not outside the bone like a plate, this area is suitable for IM nailing. The rod location will result in a shorter lever arm and lower bending moment on the device. The rod will be closer to the center of motion of the body than a plate, which is on the lateral surface of the bone further away from the center of motion of the body. Therefore, rods are subjected to smaller bending loads and less likely to result in fatigue failure. The IM rod is minimally invasive and they do not destroy the extramedullary blood supply. IM rods are load sharing so you can initiate weight bearing. IM rods are stronger than plates. You must reduce the fracture before reaming and insertion of the rod. The disadvantage is that IM rod may create varus and procurvatum deformity (flexion). There is more varus with trochanteric entry. May also have perforation at the anterior cortex distally due to mismatch between the radius of curvature of the nail and the femur.
The IM rod is not preferred in the treatment of subtrochanteric fracture that extends into the piriformis fossa or the greater trochanter. You probably need to use a fixed angle plate and probably need to avoid excessive dissection medially. You may use bone graft to avoid nonunion. Need to have bone to bone transfer medially. Try to avoid early weight bearing. The plate induces fracture healing through primary bone healing. The rod induces endochondral ossification, secondary bone healing (more abundant bone healing).
How do you use these nails? If there is enough segment of the proximal fragment that you can place a diagonal screw, this means that you have a large piece of bone and you can use a standard IM nail. If there is not enough bone segment to place a diagonal screw, then you need to place the screws on the head, called cephalomedullary nailing. If the fracture extends to the piriformis fossa or the greater trochanter, then you probably need to use a fixed angle plate.
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
https://www.utfoundation.org/foundation/home/Give_Online.aspx?sig=29
Видео Femur fracture ,Subtrochanteric fracture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
About 10% of all fractures in the proximal femur. Fracture between the lesser trochanter and a point 5 cm distal to the lesser trochanter. The subtrochanteric region is the worst area on the femur for fracture to occur. There is high compression and tensile forces in this area. Less vascularity, less healing potential and ability. This area is made of hard cortical bone that does not heal well. There is a lot of deforming forces on the proximal fragment. The subtrochanteric fracture is flexed by the iliopsoas muscle, abducted by the gluteus medius and minimus muscles, and externally rotated by the short rotator muscles. There is a high risk of implant failure. Need bone to bone transfer in this area, especially if you are going to open the fracture.
Atypical fracture is associated with bisphosphonate use, there will be thigh pain. The fracture may be seen on an MRI and usually there is no history of trauma. Using bisphosphonate for a long period of time may cause this atypical subtrochanteric fracture of the femur. The fracture may appear as a localized thickening on the lateral side of the femur. The fracture is caused by bending forces. When you bend a bone, there will be two parts: tension component (transverse component will be on the lateral side) and the compression component (oblique “spike” on the medial side: no comminution).
Typical fracture occurs due to high energy trauma such as car accidents or from a fall.
In the majority of subtrochanteric fractures, either typical or atypical, we will use a rod. Because the rod is inside the bone, and not outside the bone like a plate, this area is suitable for IM nailing. The rod location will result in a shorter lever arm and lower bending moment on the device. The rod will be closer to the center of motion of the body than a plate, which is on the lateral surface of the bone further away from the center of motion of the body. Therefore, rods are subjected to smaller bending loads and less likely to result in fatigue failure. The IM rod is minimally invasive and they do not destroy the extramedullary blood supply. IM rods are load sharing so you can initiate weight bearing. IM rods are stronger than plates. You must reduce the fracture before reaming and insertion of the rod. The disadvantage is that IM rod may create varus and procurvatum deformity (flexion). There is more varus with trochanteric entry. May also have perforation at the anterior cortex distally due to mismatch between the radius of curvature of the nail and the femur.
The IM rod is not preferred in the treatment of subtrochanteric fracture that extends into the piriformis fossa or the greater trochanter. You probably need to use a fixed angle plate and probably need to avoid excessive dissection medially. You may use bone graft to avoid nonunion. Need to have bone to bone transfer medially. Try to avoid early weight bearing. The plate induces fracture healing through primary bone healing. The rod induces endochondral ossification, secondary bone healing (more abundant bone healing).
How do you use these nails? If there is enough segment of the proximal fragment that you can place a diagonal screw, this means that you have a large piece of bone and you can use a standard IM nail. If there is not enough bone segment to place a diagonal screw, then you need to place the screws on the head, called cephalomedullary nailing. If the fracture extends to the piriformis fossa or the greater trochanter, then you probably need to use a fixed angle plate.
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
https://www.utfoundation.org/foundation/home/Give_Online.aspx?sig=29
Видео Femur fracture ,Subtrochanteric fracture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Hip or spine Pain?
Hip or spine Pain? Tennis Elbow Muscle, Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis -Everything You Need To Know -Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Tennis Elbow Muscle, Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis -Everything You Need To Know -Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Knee Pain , knee Arthritis. what is knee arthritis ?
Knee Pain , knee Arthritis. what is knee arthritis ?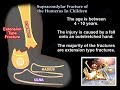 Supracondylar Fracture Of The Humerus In Children - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Supracondylar Fracture Of The Humerus In Children - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim SLAP Tear - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
SLAP Tear - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Trabecular Pattern of the Proximal Femur - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Trabecular Pattern of the Proximal Femur - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Sulcus Sign, shoulder instability
Sulcus Sign, shoulder instability Anatomy Of The Subscapularis Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Anatomy Of The Subscapularis Muscle - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Bone Cyst ,Unicameral Bone Cyst - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil
Bone Cyst ,Unicameral Bone Cyst - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Entrapment Of The Nerves Around The Shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Entrapment Of The Nerves Around The Shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Allen's Test #shorts
Allen's Test #shorts Froment's Sign - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Froment's Sign - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim NERVE INJURIES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY. Foot drop, tarsal tunnel syndrome and Morton's neuroma.
NERVE INJURIES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY. Foot drop, tarsal tunnel syndrome and Morton's neuroma. Subtalar Dislocation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Subtalar Dislocation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Upper & Lower cervical Spine Trauma, neck injury Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Upper & Lower cervical Spine Trauma, neck injury Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Anatomy Of The Upper Arm - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Anatomy Of The Upper Arm - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Nerve Compressions Of The Upper Extremity - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Nerve Compressions Of The Upper Extremity - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Spinal cord injury , ASIA Classification - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Spinal cord injury , ASIA Classification - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Actions Of The Muscles Around The Shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Actions Of The Muscles Around The Shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Intrinsic & Extrinsic Tightness of the Hand - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Intrinsic & Extrinsic Tightness of the Hand - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Shoulder Pain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Shoulder Pain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim