Urinary Incontinence for USMLE
Handwritten lecture on urinary incontinence for medical students studying for the USMLE. In particular stress incontinence, urge incontince, overflow incontinence and neuropathic incontinence. Reviewing Anatomy, Physiology, Pathophysiology, Causes, Symptoms, and Management.
PATHOLOGY
Definition of Urinary Continence is the involuntary leakage of urine. Areas of problems can be increased contraction of detrusor muscle known as urge incontinence or too much relaxation of sphincters which is overflow incontinence. Any damage to nerves leading to neurogenic bladder.
ETIOLOGY AND CAUSES
Transient causes have a nice mnemonic - DIAPPERS
Delirium - acute confusion
Infections - UTI
Atrophic vaginitis
Psychological
Excessive Urine - drinking too much fluids
Restricted mobility
Stool impaction
Drugs that may cause temporary urinary incontinence
Anti-cholinergics, anti-psychotics, anti-parkinsons, alpha agonist or alpha antagonist, Diuretics and ACE inhibitors. Calcium Channel Blockers, Sedative and Hypnotics.
INVESTIGATIONS
In the emergency room you must rule out cauda equina or cord compression. These will require MRI/CT and this is the only time you would want to do MRI/CT for urinary incontinence. Urinalysis and culture can rule out UTI. Urine cytology also helps rule out bladder cancer. Renal Function Tests are important because pathology may affect the renal function. Urodynamic studies such as uroflow studies (pressure in the bladder to the flow in urine). Postvoidal residual volume (amount of urine available after urinary and this may be done by ultrasound or catheter). Bladder complance showing how much bladder can hold. Cystourethroscopy is putting a camera into the bladder.
STRESS INCONTINENCE
Leakage with increased abdominal pressure such as cough or sneeze. Will have this classic presentation. In men the main cause is surgery (TURP) for prostate cancer. In women the causes are related to hypermobility of the sphincter since the external sphincter moves lower (usually because of vaginal delivery) and when the levator ani contracts with abdominal muscle and this can no longer occur since the levator ani is no longer surrounding the external sphincter. Sphincter deficiency is cuased by atrophy of vagina in postmenopausal women. Tend to improve with Estrogen.
Inveatigations - Pad test is used to weight for 1hr or 24 hour to see how much is leaking. Cough Test - fill bladder and ask patient to cough and look for urine. Q Tip test consists of putting a Q-tip and ask patient to rest and strain. If Q Tip moves greater than 30 degrees then the patient has a hypermobile sphincter. Urodynamic testing may show low urethral pressure
Treatment consist of weight loss, diet and Kiegle Exercises. Duloxetin (SNRI) can help symptoms. There are also surgical procedures.
URGE INCONTINENCE
Sudden feeling of urgency and before they make it to the bathroom they urinate on themselves.Due to detrosur overactivity and high sensitivity. Overactive bladder is they have urgency, frequency and may never have urge incontinence. Decrease bladder compliance. Causes consist of neurogenic causes, myogenic causes because of hypersensitive muscles. And idiopathic caueses.
Treatment consists o bladder trianing to increase capacity. Hold urine to get bladder used to increase capacity. Public muscle training and relaxation of detrusor muscle. Fluid management to control how much water they drink. Dietary changes to decrease spicy food and citrus foods. Oxybutinin and botulinum to relax the sphincters.
MIXED INCONTINENCE
Patients have stress and urge incontinence.
OVERFLOW INCONTINENCE
Bladder distention due to detrusor or sphincter problem. Bladder outlet obstruction sch as BPH, neck contraction, urethral stricture, cystocele, pelvic organ prolapse. Decreased detrusor contraction by medications that decrease detrusor contraciton. Spinal lesions and long standing overdistention weakening muscles.
Investigations to perform are postvoid residual volume measure amount of urine in bladder after voiding by ultrasound, catheter. Normal is less than 50mL and greater than 200mL is diagnostic. Anything in the middle is gray area.
Treatment is to treat underlying cause if obstructive. Non-obstructive can be treated with Chronic Intermittent catheterization.
NEUROPATHIC INCONTINENCE
Due to lesions in brain, spine or peripheral nerve. Caused by strokes, trauma, aneurysms, hemmorrhage, MS. Spinal cord lesion and cauda syndrome. May cause decrease compliance by have high bladder pressure at low filling rates causing quick leaking. Common in meninomyelocele and Upper motor Neurons. Loss of sphincter tone by cauda equina, and open external sphincter.
Investigations consists of neurologic, urodynamic, CT, MRI, and EMG.
Treatment consists of increasing compliance with anti-cholinergics oxybutinin, imipramine, botulinum. Sphincter can be used with pessary to block the sphincter and when ready urinate the cork can be removed.
Видео Urinary Incontinence for USMLE канала the study spot
PATHOLOGY
Definition of Urinary Continence is the involuntary leakage of urine. Areas of problems can be increased contraction of detrusor muscle known as urge incontinence or too much relaxation of sphincters which is overflow incontinence. Any damage to nerves leading to neurogenic bladder.
ETIOLOGY AND CAUSES
Transient causes have a nice mnemonic - DIAPPERS
Delirium - acute confusion
Infections - UTI
Atrophic vaginitis
Psychological
Excessive Urine - drinking too much fluids
Restricted mobility
Stool impaction
Drugs that may cause temporary urinary incontinence
Anti-cholinergics, anti-psychotics, anti-parkinsons, alpha agonist or alpha antagonist, Diuretics and ACE inhibitors. Calcium Channel Blockers, Sedative and Hypnotics.
INVESTIGATIONS
In the emergency room you must rule out cauda equina or cord compression. These will require MRI/CT and this is the only time you would want to do MRI/CT for urinary incontinence. Urinalysis and culture can rule out UTI. Urine cytology also helps rule out bladder cancer. Renal Function Tests are important because pathology may affect the renal function. Urodynamic studies such as uroflow studies (pressure in the bladder to the flow in urine). Postvoidal residual volume (amount of urine available after urinary and this may be done by ultrasound or catheter). Bladder complance showing how much bladder can hold. Cystourethroscopy is putting a camera into the bladder.
STRESS INCONTINENCE
Leakage with increased abdominal pressure such as cough or sneeze. Will have this classic presentation. In men the main cause is surgery (TURP) for prostate cancer. In women the causes are related to hypermobility of the sphincter since the external sphincter moves lower (usually because of vaginal delivery) and when the levator ani contracts with abdominal muscle and this can no longer occur since the levator ani is no longer surrounding the external sphincter. Sphincter deficiency is cuased by atrophy of vagina in postmenopausal women. Tend to improve with Estrogen.
Inveatigations - Pad test is used to weight for 1hr or 24 hour to see how much is leaking. Cough Test - fill bladder and ask patient to cough and look for urine. Q Tip test consists of putting a Q-tip and ask patient to rest and strain. If Q Tip moves greater than 30 degrees then the patient has a hypermobile sphincter. Urodynamic testing may show low urethral pressure
Treatment consist of weight loss, diet and Kiegle Exercises. Duloxetin (SNRI) can help symptoms. There are also surgical procedures.
URGE INCONTINENCE
Sudden feeling of urgency and before they make it to the bathroom they urinate on themselves.Due to detrosur overactivity and high sensitivity. Overactive bladder is they have urgency, frequency and may never have urge incontinence. Decrease bladder compliance. Causes consist of neurogenic causes, myogenic causes because of hypersensitive muscles. And idiopathic caueses.
Treatment consists o bladder trianing to increase capacity. Hold urine to get bladder used to increase capacity. Public muscle training and relaxation of detrusor muscle. Fluid management to control how much water they drink. Dietary changes to decrease spicy food and citrus foods. Oxybutinin and botulinum to relax the sphincters.
MIXED INCONTINENCE
Patients have stress and urge incontinence.
OVERFLOW INCONTINENCE
Bladder distention due to detrusor or sphincter problem. Bladder outlet obstruction sch as BPH, neck contraction, urethral stricture, cystocele, pelvic organ prolapse. Decreased detrusor contraction by medications that decrease detrusor contraciton. Spinal lesions and long standing overdistention weakening muscles.
Investigations to perform are postvoid residual volume measure amount of urine in bladder after voiding by ultrasound, catheter. Normal is less than 50mL and greater than 200mL is diagnostic. Anything in the middle is gray area.
Treatment is to treat underlying cause if obstructive. Non-obstructive can be treated with Chronic Intermittent catheterization.
NEUROPATHIC INCONTINENCE
Due to lesions in brain, spine or peripheral nerve. Caused by strokes, trauma, aneurysms, hemmorrhage, MS. Spinal cord lesion and cauda syndrome. May cause decrease compliance by have high bladder pressure at low filling rates causing quick leaking. Common in meninomyelocele and Upper motor Neurons. Loss of sphincter tone by cauda equina, and open external sphincter.
Investigations consists of neurologic, urodynamic, CT, MRI, and EMG.
Treatment consists of increasing compliance with anti-cholinergics oxybutinin, imipramine, botulinum. Sphincter can be used with pessary to block the sphincter and when ready urinate the cork can be removed.
Видео Urinary Incontinence for USMLE канала the study spot
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Urinary Incontinence - Stress, Urge, Overflow: Pathophysiology, Clinical correlation | USMLE | MCQs
Urinary Incontinence - Stress, Urge, Overflow: Pathophysiology, Clinical correlation | USMLE | MCQs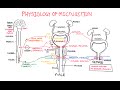 Physiology of Micturition
Physiology of Micturition Urinary incontinence - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
Urinary incontinence - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology Autonomic innervation of the Bladder
Autonomic innervation of the Bladder Renal | Micturition Reflex
Renal | Micturition Reflex USMLE® Step 1 High Yield: Nephrology: Renal Tubular Acidosis
USMLE® Step 1 High Yield: Nephrology: Renal Tubular Acidosis Understanding Sarcoidosis: A Visual Guide for Students
Understanding Sarcoidosis: A Visual Guide for Students Stop Stress Urinary Incontinence With 5 Easy Exercises
Stop Stress Urinary Incontinence With 5 Easy Exercises Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Incontinence Urinary Tract Infections: Learning Through 3 Cases - Olga Klinkova, MD
Urinary Tract Infections: Learning Through 3 Cases - Olga Klinkova, MD Kanon Health's CCRN Review: hematology & endocrine
Kanon Health's CCRN Review: hematology & endocrine Mechanical Ventilation | Most COMPREHENSIVE Explanation! 🤫
Mechanical Ventilation | Most COMPREHENSIVE Explanation! 🤫 Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women, Animation
Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women, Animation Pneumothorax - Spontaneous, Tension & Traumatic
Pneumothorax - Spontaneous, Tension & Traumatic How Does Spinal Cord Injury Effect the Bladder?
How Does Spinal Cord Injury Effect the Bladder? Aiims Norcet 2021 most repeted mcq Class-02 | Nursing Officer Live Classes
Aiims Norcet 2021 most repeted mcq Class-02 | Nursing Officer Live Classes Bladder Cancer - Overview (types, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment)
Bladder Cancer - Overview (types, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment) Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 for USMLE Step1 and USMLE Step 2
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 for USMLE Step1 and USMLE Step 2 Elimination II B Sc Nursing 1st Year II Foundations of Nursing II By Sana Mam
Elimination II B Sc Nursing 1st Year II Foundations of Nursing II By Sana Mam Hypersensitivity | USMLE
Hypersensitivity | USMLE