compartment syndrome ,Fasciotomy Wound Management - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describing fasciotomy wound management, the compartment syndrome, how to diagnose, diagnostic tests, prognosis, and treatment options.
Compartment syndrome is an urgent medical condition in which increased pressure within a closed fascial space compromises the circulation and reduces perfusion of the tissues contained in that space.
Compartment syndrome must be released within 6 hours to prevent tissue ischemia.
Compartment syndrome lasting for 8 hours or more may result in irreversible damage to the muscles and nerves within the compartment.
Clinical presentation: the extremity should be examined for:
• Pain out of proportion to the primary injury or surgery.
• Swollen and tense compartment.
• Pain with passive stretch.
The late findings for compartment syndrome:
• Paresthesia
• Pulselessness
• Pain
• Paralysis
• Pallor
Don’t wait for the late findings to establish a diagnosis.
Pressure monitoring could be used to establish or confirm the diagnosis, the threshold for fasciotomy is recommended at absolute intercompartmental pressure of 30 mmHg, or within 30mmHg of the diastolic blood pressure.
Once the diagnosis of compartment syndrome is established, fasciotomy is indicated emergently.
Decompression of all compartments with elevated pressure is mandatory.
When preforming fasciotomy of the lower leg the classic 2 incision technique is used, however, a single lateral incision has recently been introduced.
Bed side fasciotomy is an acceptable treatment option if the patient cannot be operated on in the OR.
Wound management first step:
Fasciotomy will result in a long, open wound.
The fasciotomy wound should not be closed immediately following surgery to avoid the risk of recurrent compartment syndrome.
Either wet to dry dressing or a wound vac should be applied on the area of the fasciotomy directly following surgery.
This first step is critical to preventing infection.
Wet to dry dressing: wet or moist gauze or cloth is dressed on the wound and replaced often.
Wet to dry dressing will remove wound drainage and dead tissue.
These dressings will reduce the chance of wound infection.
Wound vac: negative pressure wound therapy with a wound vac has been seen to reduce swelling, promote tissue granulation and increase perfusion in addition to keeping the wound covered, which limits the chances of wound infection.
It offers faster wound closure, reduction of scarring and a lower complication rate following fasciotomy.
Wound management second step:
This second step occurs in 48–72 hours after surgery, this step involves taking a look inside the wound to observe the muscle compartment and determine if the wound can be closed immediately or if more time is needed for the muscle swelling to decrease.
Wound closure techniques: there are 4 closing techniques following fasciotomy:
1- Delayed primary closure: is acceptable 48 hours post operatively as long as all muscle groups are confirmed viable and the swelling is reduced enough to allow closure without tension on the skin edges.
2- Split thickness skin grafting: this technique offers immediate wound coverage, however, it could require multiple operations and the scarring at the fasciotomy site and the donor site is at further disadvantage.
3- Tissue expansion by continuous traction: takes a couple of days to close the fasciotomy wound, sutures, wires, and elastic loops are used to slowly move the skin back into place, tissue expanders are used to stretch the skin on both sides of the wound and finish closing the fasciotomy wound.
4- Acell: treatment in which a powder that is obtained from pork loin urinary bladder stem cells is sprinkled onto the fasciotomy wound, this powder creates a new layer of skin in the fasciotomy wound, this technique is especially helpful when a skin graft cannot be done due to poor tissue conditions such as in children or elderly patients, Acell technique offers quick and aesthetically pleasing healing.
The clinician and patient should be aware that no single technique fits for all patients.
Everybody is different and every wound is different.
Clinical judgment and experience should be used to select the best treatment option for closure of the fasciotomy wound.
Become a friend on facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
https://www.utfoundation.org/foundation/home/Give_Online.aspx?sig=29
Видео compartment syndrome ,Fasciotomy Wound Management - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Compartment syndrome is an urgent medical condition in which increased pressure within a closed fascial space compromises the circulation and reduces perfusion of the tissues contained in that space.
Compartment syndrome must be released within 6 hours to prevent tissue ischemia.
Compartment syndrome lasting for 8 hours or more may result in irreversible damage to the muscles and nerves within the compartment.
Clinical presentation: the extremity should be examined for:
• Pain out of proportion to the primary injury or surgery.
• Swollen and tense compartment.
• Pain with passive stretch.
The late findings for compartment syndrome:
• Paresthesia
• Pulselessness
• Pain
• Paralysis
• Pallor
Don’t wait for the late findings to establish a diagnosis.
Pressure monitoring could be used to establish or confirm the diagnosis, the threshold for fasciotomy is recommended at absolute intercompartmental pressure of 30 mmHg, or within 30mmHg of the diastolic blood pressure.
Once the diagnosis of compartment syndrome is established, fasciotomy is indicated emergently.
Decompression of all compartments with elevated pressure is mandatory.
When preforming fasciotomy of the lower leg the classic 2 incision technique is used, however, a single lateral incision has recently been introduced.
Bed side fasciotomy is an acceptable treatment option if the patient cannot be operated on in the OR.
Wound management first step:
Fasciotomy will result in a long, open wound.
The fasciotomy wound should not be closed immediately following surgery to avoid the risk of recurrent compartment syndrome.
Either wet to dry dressing or a wound vac should be applied on the area of the fasciotomy directly following surgery.
This first step is critical to preventing infection.
Wet to dry dressing: wet or moist gauze or cloth is dressed on the wound and replaced often.
Wet to dry dressing will remove wound drainage and dead tissue.
These dressings will reduce the chance of wound infection.
Wound vac: negative pressure wound therapy with a wound vac has been seen to reduce swelling, promote tissue granulation and increase perfusion in addition to keeping the wound covered, which limits the chances of wound infection.
It offers faster wound closure, reduction of scarring and a lower complication rate following fasciotomy.
Wound management second step:
This second step occurs in 48–72 hours after surgery, this step involves taking a look inside the wound to observe the muscle compartment and determine if the wound can be closed immediately or if more time is needed for the muscle swelling to decrease.
Wound closure techniques: there are 4 closing techniques following fasciotomy:
1- Delayed primary closure: is acceptable 48 hours post operatively as long as all muscle groups are confirmed viable and the swelling is reduced enough to allow closure without tension on the skin edges.
2- Split thickness skin grafting: this technique offers immediate wound coverage, however, it could require multiple operations and the scarring at the fasciotomy site and the donor site is at further disadvantage.
3- Tissue expansion by continuous traction: takes a couple of days to close the fasciotomy wound, sutures, wires, and elastic loops are used to slowly move the skin back into place, tissue expanders are used to stretch the skin on both sides of the wound and finish closing the fasciotomy wound.
4- Acell: treatment in which a powder that is obtained from pork loin urinary bladder stem cells is sprinkled onto the fasciotomy wound, this powder creates a new layer of skin in the fasciotomy wound, this technique is especially helpful when a skin graft cannot be done due to poor tissue conditions such as in children or elderly patients, Acell technique offers quick and aesthetically pleasing healing.
The clinician and patient should be aware that no single technique fits for all patients.
Everybody is different and every wound is different.
Clinical judgment and experience should be used to select the best treatment option for closure of the fasciotomy wound.
Become a friend on facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/drebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Donate to the University of Toledo Foundation Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Endowed Chair Fund:
https://www.utfoundation.org/foundation/home/Give_Online.aspx?sig=29
Видео compartment syndrome ,Fasciotomy Wound Management - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Acute and chronic leg Compartment Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Acute and chronic leg Compartment Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Compartment syndrome - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
Compartment syndrome - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology Compartment Syndrome - Overview (signs and symptoms, pathophysiology, treatment)
Compartment Syndrome - Overview (signs and symptoms, pathophysiology, treatment) Piriformis Syndrome A Hidden Cause of Sciatica - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Piriformis Syndrome A Hidden Cause of Sciatica - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Cervical fascia
Cervical fascia Compartment Syndrome Nursing NCLEX Review Question on Interventions and Neurovascular Assessment
Compartment Syndrome Nursing NCLEX Review Question on Interventions and Neurovascular Assessment Compartment Syndrome Of The Hand & Finger - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Compartment Syndrome Of The Hand & Finger - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim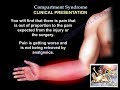 Compartment Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Compartment Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Osteochondroma , solitary and multiple . Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Osteochondroma , solitary and multiple . Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Bedside Fasciotomy For Compartment Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Bedside Fasciotomy For Compartment Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Skill Station: Compartment Syndrome & Fasciotomy
Skill Station: Compartment Syndrome & Fasciotomy Measuring Compartment Pressure
Measuring Compartment Pressure Compartment Syndrome Of The Forearm - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Compartment Syndrome Of The Forearm - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim MRI of the Brachial Plexus
MRI of the Brachial Plexus Ankle Fracture Maisonneuve Fracture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Ankle Fracture Maisonneuve Fracture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim General Trauma Management,the injured patient- Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
General Trauma Management,the injured patient- Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Principles of Fracture Fixation | Orthopedic Basics
Principles of Fracture Fixation | Orthopedic Basics Compartment Syndrome
Compartment Syndrome psoas Abscess infection, A Diagnostic Dilemma - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
psoas Abscess infection, A Diagnostic Dilemma - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Nonunion of the Humerus - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Nonunion of the Humerus - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim