Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei - Nuclear Reactor
Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei - Nuclear Reactor
Visit https://learnfatafat.com/courses/physics-class-12-cbse/ to access 226+ class 12 Physics videos.
Nuclear reactor helps to carry out controlled chain reaction and also produce energy in sustained manner. Produced energy can be used to produce electric energy. In this article we will discuss about nuclear reactor, its parts and their function.
Nuclear Fuel
Nuclear fuel is the fissionable material used in nuclear reactor. Generally, U-233, U- 235 and Pu- 239 is taken as nuclear fuel in form of cylindrical rods arranged in regular pattern in the active reactor core. However, the volume of core is filled with material of light nuclei called moderator. The geometry of core is such that on average out every three neutrons produced per fission. one neutron is used to trigger next fission. However, other neutrons are lost without undergoing any fission.
Moderator
Slow moving neutron have more tendency to facilitate fission reaction rather than the fast moving neutrons. Average energy of neutron produced in fission of U-235 is 2 MeV. these are the fast neutrons and have low tendency to cause fission. In order to facilitate fission reaction there is need to slow down the neutrons. The job is done by moderator in nuclear reactor, by transferring the energy with elastic collision to lighter nuclei. In nuclear reactors water, solid graphite or heavy water are used as moderators.
Control Rods
Nuclear reaction if not controlled can cause massive explosion. Multiplication factor K helps us to determine if reaction is in control or not. K=1 is required for sustained energy production. If K exceeds unity control rods made of boron or cadmium are inserted in the reactor core upto desirable length. The rods have the ability to absorb neutrons. Therefore, the nuclear reaction can be controlled thereby bringing down the multiplication factor down unity.
Safety Rod
In addition to control rods, the reactors are provided with safety rods. These rods can be inserted into reactor in order to bring value of K below unity. Hence, it keeps power generation safe.
Coolant
Heat produced in the core is absorbed by coolant. Later this energy is passed to water in heat exchanger. Thus, it produces steam. The steam is used to drive turbine coupled with electric generator and thus, electric energy is produced. In general water or heavy water is used as coolant. In case of high temperature, liquid sodium is used as coolant.
Shielding
Nuclear fission produces hazardous radiations, therefore, nuclear reactor is kept in concrete walls of 2 m to 2.5 m thick. This prevents radiations from reaching outside environment.
Working
The cadmium rods are slowly removed so that slow moving neutrons can cause fission of U-235 nuclei generating energy . In the primary-loop, coolant absorb energy . The energy is transported at high temperature and pressure to the steam generator in secondary loop where evaporation of water takes place. Evaporation provides high-pressure steam to operate the turbine and in turn, drives the electric generator. The low-pressure steam from the turbine is cooled and condensed to water and forced back into the steam generator.
Advantages and disadvantages of nuclear reactor
It is advantageous because in very small quantity of fuel it produce large energy . However, the disadvantage is that there is problem of disposal of radioactive nuclear waste and maintenance of equipment.
You can also watch our all 12th Physics videos on https://learnfatafat.com/product-category/cbse-class-12/
CBSE Class 12 Physics syllabus -
Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields
Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Chapter 3 Current Electricity
Chapter 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism
Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter
Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction
Chapter 7 Alternating Current
Chapter 8 Electromagnetic Waves
Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Chapter 10 Wave Optics
Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Chapter 12 Atoms
Chapter 13 Nuclei
Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Chapter 15 Communication Systems
Видео Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei - Nuclear Reactor канала LearnFatafat
Visit https://learnfatafat.com/courses/physics-class-12-cbse/ to access 226+ class 12 Physics videos.
Nuclear reactor helps to carry out controlled chain reaction and also produce energy in sustained manner. Produced energy can be used to produce electric energy. In this article we will discuss about nuclear reactor, its parts and their function.
Nuclear Fuel
Nuclear fuel is the fissionable material used in nuclear reactor. Generally, U-233, U- 235 and Pu- 239 is taken as nuclear fuel in form of cylindrical rods arranged in regular pattern in the active reactor core. However, the volume of core is filled with material of light nuclei called moderator. The geometry of core is such that on average out every three neutrons produced per fission. one neutron is used to trigger next fission. However, other neutrons are lost without undergoing any fission.
Moderator
Slow moving neutron have more tendency to facilitate fission reaction rather than the fast moving neutrons. Average energy of neutron produced in fission of U-235 is 2 MeV. these are the fast neutrons and have low tendency to cause fission. In order to facilitate fission reaction there is need to slow down the neutrons. The job is done by moderator in nuclear reactor, by transferring the energy with elastic collision to lighter nuclei. In nuclear reactors water, solid graphite or heavy water are used as moderators.
Control Rods
Nuclear reaction if not controlled can cause massive explosion. Multiplication factor K helps us to determine if reaction is in control or not. K=1 is required for sustained energy production. If K exceeds unity control rods made of boron or cadmium are inserted in the reactor core upto desirable length. The rods have the ability to absorb neutrons. Therefore, the nuclear reaction can be controlled thereby bringing down the multiplication factor down unity.
Safety Rod
In addition to control rods, the reactors are provided with safety rods. These rods can be inserted into reactor in order to bring value of K below unity. Hence, it keeps power generation safe.
Coolant
Heat produced in the core is absorbed by coolant. Later this energy is passed to water in heat exchanger. Thus, it produces steam. The steam is used to drive turbine coupled with electric generator and thus, electric energy is produced. In general water or heavy water is used as coolant. In case of high temperature, liquid sodium is used as coolant.
Shielding
Nuclear fission produces hazardous radiations, therefore, nuclear reactor is kept in concrete walls of 2 m to 2.5 m thick. This prevents radiations from reaching outside environment.
Working
The cadmium rods are slowly removed so that slow moving neutrons can cause fission of U-235 nuclei generating energy . In the primary-loop, coolant absorb energy . The energy is transported at high temperature and pressure to the steam generator in secondary loop where evaporation of water takes place. Evaporation provides high-pressure steam to operate the turbine and in turn, drives the electric generator. The low-pressure steam from the turbine is cooled and condensed to water and forced back into the steam generator.
Advantages and disadvantages of nuclear reactor
It is advantageous because in very small quantity of fuel it produce large energy . However, the disadvantage is that there is problem of disposal of radioactive nuclear waste and maintenance of equipment.
You can also watch our all 12th Physics videos on https://learnfatafat.com/product-category/cbse-class-12/
CBSE Class 12 Physics syllabus -
Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields
Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Chapter 3 Current Electricity
Chapter 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism
Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter
Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction
Chapter 7 Alternating Current
Chapter 8 Electromagnetic Waves
Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Chapter 10 Wave Optics
Chapter 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Chapter 12 Atoms
Chapter 13 Nuclei
Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Chapter 15 Communication Systems
Видео Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei - Nuclear Reactor канала LearnFatafat
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Working of Nuclear Reactor
Working of Nuclear Reactor Nuclear Physics
Nuclear Physics 5. NUCLEAR FISSION | NUCLEAR REACTOR | NUCLEI CLASS 12
5. NUCLEAR FISSION | NUCLEAR REACTOR | NUCLEI CLASS 12 Top 5 Amazing Nuclear Reactor Startups
Top 5 Amazing Nuclear Reactor Startups Nuclear Fission
Nuclear Fission 3 Reasons Why Nuclear Energy Is Awesome! 3/3
3 Reasons Why Nuclear Energy Is Awesome! 3/3 Nuclear Reactor (Part 1) - Nuclei | Class 12 Physics
Nuclear Reactor (Part 1) - Nuclei | Class 12 Physics FSc Physics Book 2, Ch 21 - Nuclear Reactor - Inter Part 2 Physics
FSc Physics Book 2, Ch 21 - Nuclear Reactor - Inter Part 2 Physics Welcome to Darlington Nuclear Generating Station
Welcome to Darlington Nuclear Generating Station Nuclei Introduction | Radioactive Decay | Class 12 Physics | NEET 2020 | NEET Physics | Gaurav sir
Nuclei Introduction | Radioactive Decay | Class 12 Physics | NEET 2020 | NEET Physics | Gaurav sir How I built a nuclear reactor at the age of 13 | Jamie Edwards | TEDxCERN
How I built a nuclear reactor at the age of 13 | Jamie Edwards | TEDxCERN FSc Physics Book 2, Ch 21 - Fusion Reactions - Inter Part 2 Physics
FSc Physics Book 2, Ch 21 - Fusion Reactions - Inter Part 2 Physics Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant - India's Nuclear Pride
Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant - India's Nuclear Pride Nuclear Fusion | Fusion energy explained with Hydrogen atom example | Physics animation video
Nuclear Fusion | Fusion energy explained with Hydrogen atom example | Physics animation video Nuclear Reactor - Understanding how it works | Physics Elearnin
Nuclear Reactor - Understanding how it works | Physics Elearnin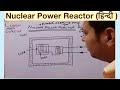 Nuclear Power Reactor (हिन्दी )
Nuclear Power Reactor (हिन्दी ) Nuclear Power Plant Safety Systems
Nuclear Power Plant Safety Systems 🔴 Nuclear Fission (Part 3) || NUCLEAR REACTOR in HINDI
🔴 Nuclear Fission (Part 3) || NUCLEAR REACTOR in HINDI Nuclear Reactor | Chapter - Nucleus | Physics | Class 12
Nuclear Reactor | Chapter - Nucleus | Physics | Class 12