Peptic Ulcer for USMLE Step 1 and USMLE Step 2
Handwritten lecture on Peptic Ulcer Disease for USMLE Step 1 and USMLE Step 2. Will be covering pathophysiology, pathogenesis, symptoms and treatment.
PHYSIOLOGY OF PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
There are many important cells responsible for maintaining stomach pH.
Parietal cells secrete hydrogen ions and maintain low pH
Chief Cells secrete pepsinogen which is converted to pepsin when reaction with hydrogen ions and breakdown proteins.
Enterochromaffin cells secrete histamine which increases parietal cells to secrete more acid.
G Cells secrete gastrin which increases activity of parietal cells
D Cells secrete somatostatin which deactivates parietal cells.
Mucous cell found in epithelial layer secrete mucin which protect the stomach lining from acidity.
Abnormalities in the functions of any of these cells can lead to peptic ulcer disease.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
Helicobacter pylori is a bacteria which can attach to the stomach lining and produce peptic ulcer disease. The bacteria can survive in acidic environment where it produces urease to convert urea to ammonia and increase local pH. It can also secrete proteases and phosholipases. All of these factors lead to peptic ulcer disease. Its more common in crowded condition because of oral oral or fecal oral transmission. H. Pylori almost always causes chronic gastritis and rarely causes peptic ulcer disease.
NSAIDs can also lead to peptic ulcer disease by decreasing levels of prostaglandin. This decreases the protection of the stomach lining. Even taking 75mg day can lead to peptic ulcer disease.
Other causes of peptic ulcer disease include smoking, genetic, diet, head trauma (Cushing's Ulcer), Burns (Curling's ulcer). Also chronic conditionis such as chronic pulmonary disease, chronic renal failure, cirrhosis can also lead to peptic ulcer disease.
SYMPTOMS OF PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
Epigastric pain is most common complaint, but there are many differential diagnosis.
Duodenal ulcer occur 90min to 3 hours after eating. And food can releive pain. And they awake from sleep due to pain. Gastric ulcer patients have pain with food.
Complications of peptic ulcer disease include GI bleeding, Perforation and gastric outlet obstruction. Also patients can get carcinoma or MALToma.
Alarm symptoms include weight loss, odynophagia, recurrent vomiting, jaundice, GI Bleeding, Palpable mass, history of cancer or greater than 45 years old. All of these patients get endoscopy. If there is ulcer then take biopsy to rule out cancer or confirm peptic ulcer disease.
Without alarm symptoms do urea breathe test or fecal antigen test. But patient could not have had PPI or antibiotics within last 28 days. If urea breathe test is positive then give triple therapy or give PPI.
TREATMENT OF PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
H. Pylori give triple therapy, omeprazole, clarithromycin, metronidzole or Amoxicillin. Check in 14 days. If failure give Quadruple therapy, Omeprazole, Bismuth, Metronidazole, Tetracycline. If failure again then do culture and sensitivity.
NSAID induced peptic ulcer, the best treatment is to discontinue NSAID. If not possibel than switch to diclofenac or ibuprofen.
Surgical options for peptic ulcer include vagatomy or antrectomy.
Видео Peptic Ulcer for USMLE Step 1 and USMLE Step 2 канала the study spot
PHYSIOLOGY OF PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
There are many important cells responsible for maintaining stomach pH.
Parietal cells secrete hydrogen ions and maintain low pH
Chief Cells secrete pepsinogen which is converted to pepsin when reaction with hydrogen ions and breakdown proteins.
Enterochromaffin cells secrete histamine which increases parietal cells to secrete more acid.
G Cells secrete gastrin which increases activity of parietal cells
D Cells secrete somatostatin which deactivates parietal cells.
Mucous cell found in epithelial layer secrete mucin which protect the stomach lining from acidity.
Abnormalities in the functions of any of these cells can lead to peptic ulcer disease.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
Helicobacter pylori is a bacteria which can attach to the stomach lining and produce peptic ulcer disease. The bacteria can survive in acidic environment where it produces urease to convert urea to ammonia and increase local pH. It can also secrete proteases and phosholipases. All of these factors lead to peptic ulcer disease. Its more common in crowded condition because of oral oral or fecal oral transmission. H. Pylori almost always causes chronic gastritis and rarely causes peptic ulcer disease.
NSAIDs can also lead to peptic ulcer disease by decreasing levels of prostaglandin. This decreases the protection of the stomach lining. Even taking 75mg day can lead to peptic ulcer disease.
Other causes of peptic ulcer disease include smoking, genetic, diet, head trauma (Cushing's Ulcer), Burns (Curling's ulcer). Also chronic conditionis such as chronic pulmonary disease, chronic renal failure, cirrhosis can also lead to peptic ulcer disease.
SYMPTOMS OF PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
Epigastric pain is most common complaint, but there are many differential diagnosis.
Duodenal ulcer occur 90min to 3 hours after eating. And food can releive pain. And they awake from sleep due to pain. Gastric ulcer patients have pain with food.
Complications of peptic ulcer disease include GI bleeding, Perforation and gastric outlet obstruction. Also patients can get carcinoma or MALToma.
Alarm symptoms include weight loss, odynophagia, recurrent vomiting, jaundice, GI Bleeding, Palpable mass, history of cancer or greater than 45 years old. All of these patients get endoscopy. If there is ulcer then take biopsy to rule out cancer or confirm peptic ulcer disease.
Without alarm symptoms do urea breathe test or fecal antigen test. But patient could not have had PPI or antibiotics within last 28 days. If urea breathe test is positive then give triple therapy or give PPI.
TREATMENT OF PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
H. Pylori give triple therapy, omeprazole, clarithromycin, metronidzole or Amoxicillin. Check in 14 days. If failure give Quadruple therapy, Omeprazole, Bismuth, Metronidazole, Tetracycline. If failure again then do culture and sensitivity.
NSAID induced peptic ulcer, the best treatment is to discontinue NSAID. If not possibel than switch to diclofenac or ibuprofen.
Surgical options for peptic ulcer include vagatomy or antrectomy.
Видео Peptic Ulcer for USMLE Step 1 and USMLE Step 2 канала the study spot
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Gastric Acid Physiology (Secretion, Ulcers, Acid Reflux and Treatment)
Gastric Acid Physiology (Secretion, Ulcers, Acid Reflux and Treatment) Liver Explained Clearly - Pathophysiology, LFTs, Hepatic Diseases
Liver Explained Clearly - Pathophysiology, LFTs, Hepatic Diseases Drugs used in Peptic ulcer disease
Drugs used in Peptic ulcer disease USMLE GIT 6: Stomach Pathology (H. Pylori, Ulcers and more)
USMLE GIT 6: Stomach Pathology (H. Pylori, Ulcers and more) Diabetic Retinopathy for USMLE Step 1 and USMLE Step 2
Diabetic Retinopathy for USMLE Step 1 and USMLE Step 2 Coronary Artery Disease - Ischemic Heart Disease - Angina
Coronary Artery Disease - Ischemic Heart Disease - Angina Extrapulmonary TB
Extrapulmonary TB Pharmacology - Antihypertensives
Pharmacology - Antihypertensives Peptic ulcer disease - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
Peptic ulcer disease - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology Liver Anatomy and Blood Supply
Liver Anatomy and Blood Supply Epidural Hematoma, Subdural hematoma, Subarachnoid hematoma, Intracerebral hemorrhage
Epidural Hematoma, Subdural hematoma, Subarachnoid hematoma, Intracerebral hemorrhage Stomach (anatomy)
Stomach (anatomy) Leg Venous Disease
Leg Venous Disease Inflammatory Bowel Disease Part 1
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Part 1 Immunology - Helper T cells CD4+ and B cells - Lymphocytes
Immunology - Helper T cells CD4+ and B cells - Lymphocytes Acute Liver Failure
Acute Liver Failure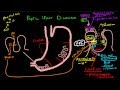 Peptic Ulcer Disease Pathophysiology
Peptic Ulcer Disease Pathophysiology Dr. Pritesh Singh Discusses "STOMACH"
Dr. Pritesh Singh Discusses "STOMACH" Peptic Ulcer Disease (Gastric vs. Duodenal Ulcers) | Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Peptic Ulcer Disease (Gastric vs. Duodenal Ulcers) | Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 for USMLE Step1 and USMLE Step 2
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 for USMLE Step1 and USMLE Step 2