Supracondylar Fracture Of The Humerus In Children - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes supracondylar fractures of the humerus.
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
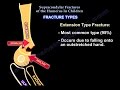
Supracondylar fracture of the humerus occurs in children between the ages of 4 - 10 years. The injury is caused by a fall onto an outstretched hand. The majority of the fractures are extension type fractures. Type III is a displaced fracture and it carries a high incidence of neurovascular deficit and compartment syndrome. Compartment syndrome may not develop right away, it may take hours to develop. The physician should not confuse compartment syndrome with the arterial injury. You can have arterial injury and compartment syndrome or compartment syndrome without arterial injury, and in this case you will need fasciotomy to release the compartment syndrome. The anterior interosseous nerve is involved in the extension type injury. The patient cannot do the O.K. sign. If you have an extension type injury and you find that the patient has an ulnar nerve palsy after surgery, then it is probably not due to the extension type injury, but rather is due to the medial pin that may have affected the ulnar nerve. In the flexion type injury, the ulnar nerve injury is more common.
CLASSIFICATION
GARTLAND CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
- TYPE I Nondisplaced
- TYPE II Angulated with an intact posterior cortex
- TYPE III Displaced
TREATMENT
Type I - Immobilize.
Type II & Type III - Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. If you cannot get the alignment correct, then do open reduction.
You will place two or three lateral pins. If a medial pin is needed, be careful of the position of the ulnar nerve. Use open incision to introduce the medial pin. Have the elbow in extension, not in flexion, when you place the medial pin because this will relax the ulnar nerve. When you use the pins, do diversion pins. The cross pins configuration, medial and lateral pins, gives the maximum rotatory stability. The crossing should be approximately 2 cm proximal to the fracture. Normally we use two diversion lateral pins and adding a third pin will increase the stiffness in case of medial comminution. Avoid malposition of the fragments because it can lead to malunion and cubitus varus. Very rarely you may have to do corrective osteotomy for the cubitus varus (it is only a cosmetic problem, not a functional problem).
If you have a pulseless, pink hand or a pulseless, white hand, then there is decreased perfusion. You will need to do emergency closed reduction and pinning. If closed reduction cannot be done, then you will do open reduction and pinning. After this, if the hand is pink and warm, then you observe. Observe for capillary refill, for temperature, and for color with the elbow in some flexion, but not in hyperflexion. If after the closed reduction and pinning the hand continues to be white and cold, you will do exploration of the artery. A pulseless, white hand from the beginning and you reduced and pinned the fracture, but the hand continues to be white, then you need to explore and repair the artery. You will repair the artery through an anterior approach and you will do fasciotomy after that. Initially, if the circulation was good, but after reduction and fixation you have a pulseless, white hand, then you need to unreduce the fracture fixation. When you have a nerve injury, observe the patient, do not explore the nerve! The recovery will start in about 6 - 12 weeks and the majority are completed in 4 - 5 months. Do not explore the nerve in closed fractures! What if the patient had an ulnar nerve palsy after surgery and the patient did not have that before surgery? Then remove the medial pin and observe.
Видео Supracondylar Fracture Of The Humerus In Children - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Follow me on twitter:
https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC
Supracondylar fracture of the humerus occurs in children between the ages of 4 - 10 years. The injury is caused by a fall onto an outstretched hand. The majority of the fractures are extension type fractures. Type III is a displaced fracture and it carries a high incidence of neurovascular deficit and compartment syndrome. Compartment syndrome may not develop right away, it may take hours to develop. The physician should not confuse compartment syndrome with the arterial injury. You can have arterial injury and compartment syndrome or compartment syndrome without arterial injury, and in this case you will need fasciotomy to release the compartment syndrome. The anterior interosseous nerve is involved in the extension type injury. The patient cannot do the O.K. sign. If you have an extension type injury and you find that the patient has an ulnar nerve palsy after surgery, then it is probably not due to the extension type injury, but rather is due to the medial pin that may have affected the ulnar nerve. In the flexion type injury, the ulnar nerve injury is more common.
CLASSIFICATION
GARTLAND CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
- TYPE I Nondisplaced
- TYPE II Angulated with an intact posterior cortex
- TYPE III Displaced
TREATMENT
Type I - Immobilize.
Type II & Type III - Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. If you cannot get the alignment correct, then do open reduction.
You will place two or three lateral pins. If a medial pin is needed, be careful of the position of the ulnar nerve. Use open incision to introduce the medial pin. Have the elbow in extension, not in flexion, when you place the medial pin because this will relax the ulnar nerve. When you use the pins, do diversion pins. The cross pins configuration, medial and lateral pins, gives the maximum rotatory stability. The crossing should be approximately 2 cm proximal to the fracture. Normally we use two diversion lateral pins and adding a third pin will increase the stiffness in case of medial comminution. Avoid malposition of the fragments because it can lead to malunion and cubitus varus. Very rarely you may have to do corrective osteotomy for the cubitus varus (it is only a cosmetic problem, not a functional problem).
If you have a pulseless, pink hand or a pulseless, white hand, then there is decreased perfusion. You will need to do emergency closed reduction and pinning. If closed reduction cannot be done, then you will do open reduction and pinning. After this, if the hand is pink and warm, then you observe. Observe for capillary refill, for temperature, and for color with the elbow in some flexion, but not in hyperflexion. If after the closed reduction and pinning the hand continues to be white and cold, you will do exploration of the artery. A pulseless, white hand from the beginning and you reduced and pinned the fracture, but the hand continues to be white, then you need to explore and repair the artery. You will repair the artery through an anterior approach and you will do fasciotomy after that. Initially, if the circulation was good, but after reduction and fixation you have a pulseless, white hand, then you need to unreduce the fracture fixation. When you have a nerve injury, observe the patient, do not explore the nerve! The recovery will start in about 6 - 12 weeks and the majority are completed in 4 - 5 months. Do not explore the nerve in closed fractures! What if the patient had an ulnar nerve palsy after surgery and the patient did not have that before surgery? Then remove the medial pin and observe.
Видео Supracondylar Fracture Of The Humerus In Children - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim канала nabil ebraheim
Показать
Комментарии отсутствуют
Информация о видео
Другие видео канала
 Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus In Children
Supracondylar Fractures Of The Humerus In Children Monteggia Fracture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Monteggia Fracture - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Rotator Cuff Muscles - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Rotator Cuff Muscles - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Supracondylar fracture - radiology video tutorial (x-ray)
Supracondylar fracture - radiology video tutorial (x-ray) Scratch Collapse Test for testing nerve injury - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Scratch Collapse Test for testing nerve injury - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Supracondylar humerus fracture , pulseless hand - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Supracondylar humerus fracture , pulseless hand - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Genu Valgus - Dr Ravi Chauhan
Genu Valgus - Dr Ravi Chauhan Guyan's Canal Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Guyan's Canal Syndrome - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Pediatric fractures ,Upper Extremity Review - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Pediatric fractures ,Upper Extremity Review - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Tendon Ruptures Around The Shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Tendon Ruptures Around The Shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Management of Limb Length Discrepancy for the Orthopaedic Exams
Management of Limb Length Discrepancy for the Orthopaedic Exams Humerus, Distal—Pediatric Supracondylar Fracture 13-M_3.1 III and IV—Fracture Management
Humerus, Distal—Pediatric Supracondylar Fracture 13-M_3.1 III and IV—Fracture Management Osteonecrosis Of The Hip Stages & Treatment - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil
Osteonecrosis Of The Hip Stages & Treatment - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Shoulder Pain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Shoulder Pain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Common Types Of Distal Radius Fractures - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Common Types Of Distal Radius Fractures - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures by Dr Todd Mason
Pediatric Supracondylar Fractures by Dr Todd Mason Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Ankle fractures , minimally invasive Fixation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Ankle fractures , minimally invasive Fixation - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim Femoral Neck Fracture Classification - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Femoral Neck Fracture Classification - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim The outlier variety of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children-How to reduce the irreducible one
The outlier variety of Supracondylar Humerus Fractures in Children-How to reduce the irreducible one